Winter Melon: Nutrition, Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
Explore the nutritional value, benefits, uses, and precautions of winter melon, a hydrating fruit favored for its remarkable health advantages.
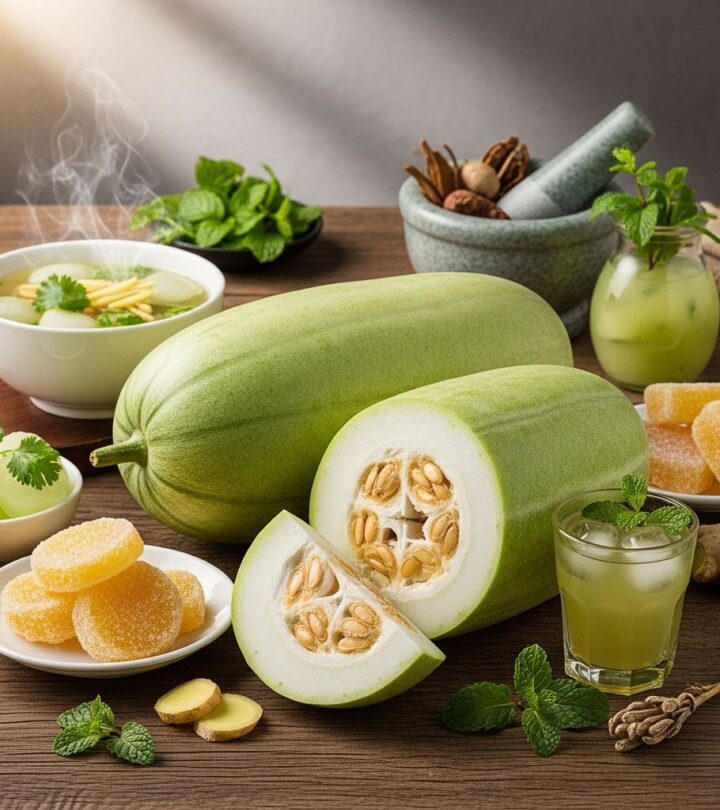

Image: ShutterStock
Winter Melon: An Overview
Winter melon (Benincasa hispida), also known as ash gourd or white gourd, is a popular fruit vegetable found across Asia. Known for its pale green or white waxy exterior and mild taste, winter melon stands out for its remarkable nutritional composition, versatile culinary applications, and traditional medicinal uses. Whether consumed as a vegetable, juice, or medicinal ingredient, winter melon has gained attention as a beneficial addition to a balanced diet.
What is Winter Melon?
Winter melon is a large, oblong fruit from the Cucurbitaceae family. Despite its name, winter melon is not a true melon but shares similarities in texture and water content. The fruit matures to a white, waxy coating, aiding storage during winter, which led to its common naming.
- Common Names: Ash gourd, white gourd, Chinese melon, Petha (in India).
- Physical Characteristics: Pale green to white skin, chalky flesh, mild flavor.
- Primary Origins: South and East Asia; used in Chinese, Indian, Vietnamese, and Thai cuisines.
Winter Melon Nutrition Facts
Winter melon is celebrated for being low in calories yet rich in hydrating water, fiber, and several essential vitamins and minerals. Here’s a breakdown per 100 grams:
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value (DV) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 13 kcal | 1% |
| Water | ~96 g | — |
| Carbohydrates | 3 g | 1% |
| Protein | 0.4 g | 1% |
| Total Fat | 0.2 g | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3 g | 12% |
| Vitamin C | 13 mg | 14% |
| Zinc | 0.6 mg | 6% |
| Iron | 0.4 mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 19 mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 10 mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 19 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0.04 mg | 3% |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0.11 mg | 8% |
| Niacin (B3) | 0.4 mg | 2% |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.13 mg | 2% |
| Folate | 5 mcg | 1% |
| Sodium | 111 mg | 5% |
Winter melon also contains small amounts of antioxidants such as flavonoids and carotenes, and minerals like potassium, manganese, and copper.
Top Health Benefits of Winter Melon
Winter melon is widely recognized for its nourishing profile and positive effects on health. Here are some science-backed benefits:
1. Hydration Boost
- Composed of over 90% water, winter melon is excellent for hydrating the body and replenishing lost fluids, especially during hot weather.
- Makes a refreshing juice for natural hydration.
2. Weight Management
- Its low calorie and high fiber content promote satiety, making it suitable for weight loss diets.
3. Immunity and Disease Protection
- Vitamin C boosts white blood cell production, strengthening the immune system.
- Zinc supports cellular function and immune responses.
4. Digestive System Support
- Dietary fiber aids digestion, helps prevent constipation, bloating, and other gastrointestinal issues.
- May lower cholesterol levels and support gut health.
5. Energy Production & Metabolism
- Contains riboflavin (Vitamin B2), vital for converting food into usable energy and maintaining hormonal balance.
6. Cardiovascular Health
- Potassium acts as a vasodilator, helping reduce blood pressure and mitigate risk of heart conditions.
- Vitamin C and antioxidants contribute to vascular integrity.
7. Cognitive Function
- Iron aids in hemoglobin production and blood circulation, ensuring proper oxygen flow to the brain.
- May improve memory, learning, and protect against anemia.
8. Vision Support
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) deficiency is linked to vision problems; winter melon helps meet daily needs, minimizes oxidative stress, and reduces macular degeneration risk.
9. Detoxification and Liver Health
- Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, supporting liver detoxification and overall cellular health.
Traditional and Medicinal Uses
Winter melon is valued in both traditional medicine and culinary culture:
- Ayurveda: Used as a cooling agent to balance body heat and treat peptic ulcers.
- Chinese Medicine: Commonly prescribed for managing fevers, detoxification, and urinary disorders.
- Folk Remedies: Juice and pulp are applied externally for skin ailments and inflammation.
The high water, nutritional content, and gentle flavor make winter melon suitable for people recovering from illness or those needing a soothing, easy-to-digest food.
Culinary Uses of Winter Melon
Winter melon is a staple ingredient in Asian cuisine thanks to its mild taste and adaptability. Popular ways to enjoy winter melon include:
- Soups and Stews: Commonly used in Chinese winter melon soup with pork or chicken.
- Sweets: In India, candied winter melon is known as petha and enjoyed as a traditional dessert.
- Juices and Drinks: Hydrating winter melon juice is popular in tropical regions.
- Stir-fries and Curries: Works well with spices, vegetables, and meats.
- Pickles: Used for tangy, long-lasting pickled preserves.
Tip: When buying winter melon, choose firm, heavy fruits with unblemished skin. Store in a cool, dry place or refrigerate once cut.
How to Prepare and Eat Winter Melon
- Peel off the hard waxy skin and discard seeds before cooking.
- Slice or cube the flesh for soups, stews, or sweet dishes.
- Winter melon absorbs flavors well, making it ideal for brothy or spicy recipes.
- Juicing: Blend with water and strain for a refreshing drink.
- Boiling or steaming preserves nutrients better than frying.
Winter Melon Recipes
Here are simple ways to incorporate winter melon into your diet:
- Winter Melon Soup: Simmer winter melon cubes with pork bones, ginger, and green onions.
- Ash Gourd Juice: Blend peeled melon with water and a touch of lemon; strain and serve chilled.
- Indian Petha: Cook melon cubes with sugar and cardamom, boil until pieces are translucent.
Choosing and Storing Winter Melon
- Selection: Pick melons that have a consistent waxy surface and feel heavy for their size.
- Storage: Uncut winter melon may last weeks in cool, dry storage; cut portions should be refrigerated and used within a few days.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Winter melon is usually safe for most people when consumed in moderate food quantities, but certain precautions should be considered:
- Allergic Reactions: Rare, but some individuals may experience allergic effects; discontinue use and seek advice if symptoms occur.
- Bloating and Loose Stool: High fiber can cause mild digestive discomfort if overconsumed.
- Pregnancy and Medication: Consult a doctor before using large amounts medicinally, especially if pregnant or on blood pressure medications due to melon’s potassium content.
- Traditional Use vs. Modern Research: While traditional medicinal uses abound, more scientific studies are needed for confirmation. Always consider professional advice for therapeutic use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is winter melon suitable for diabetics?
A: Yes, due to its low glycemic index and high fiber, winter melon is appropriate for diabetics and may help regulate blood sugar levels.
Q: Can winter melon help with weight loss?
A: Winter melon’s high fiber content increases satiety and reduces overall calorie intake, supporting weight loss efforts.
Q: Does winter melon interact with medications?
A: It is generally safe in food forms, but high intake may interact with diuretics or blood pressure medication. Consult a healthcare provider if concerned.
Q: What is the best way to consume winter melon for health benefits?
A: Eating it cooked in soups or raw as juice offers hydration, fibers, and antioxidants; avoid adding excessive sugar or fat to recipes.
Q: How do I know if a winter melon is ripe?
A: Look for a dull, waxy coating and firm, white flesh. Unripe melons have shinier skins or are softer to touch.
Key Takeaways
- Winter melon is low in calories, high in water and fiber, and packed with antioxidants.
- It supports digestion, immunity, heart health, cognitive function, and hydration.
- Commonly used in Asian soups, juices, desserts, and traditional medicines.
- It is safe for most people but consult a doctor before high therapeutic use.
References
- FoodStruct.com: Nutritional Data
- Lybrate.com: Benefits & Side Effects
- OrganicFacts.net: Health Benefits
- Dr. Axe: Nutrition and Uses
- Healthline: Nutrition, Benefits & Uses
- The Joint: Heart & Cognitive Function
- Isha Sadhguru: Mineral Composition
- Times of India: Benefits of Juice
References
- https://foodstruct.com/food/winter-melon
- https://www.lybrate.com/topic/winter-melon-petha-benefits-and-side-effects
- https://www.organicfacts.net/health-benefits/vegetable/winter-melon-benefits-nutritional-value.html
- https://draxe.com/nutrition/winter-melon/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ash-gourd
- https://www.thejoint.com/california/north-hollywood/noho-west-31198/337023-winter-melon-is-good-for-heart-cognitive-function
- https://isha.sadhguru.org/en/blog/article/ash-gourd-benefits-recipes
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/this-is-what-happens-when-you-drink-winter-melon-juice-in-summers/photostory/121779138.cms
Read full bio of Medha Deb