Irregular Periods: 14 Causes And 10 Effective Remedies
Discover effective natural solutions to balance your cycle and enhance overall wellness today!

Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
It is not unusual to miss a period or have heavy bleeding once in a while. But if it happens frequently, it could be annoying as you cannot be prepared for it. Moreover, if you are planning to start a family, your irregular period will make it difficult to identify your fertile days.

So, when can you call a period to be irregular? What are the reasons behind it, and how do they impact your conception? MomJunction answers all these questions and tells you everything you need to know about irregular periods.
Irregular Periods And Their Types
The typical length of a menstrual cycle is 28 days. The period may come early or late and can be slightly shorter or longer than 28 days. On an average, you may get your period anytime between 24 and 38 days, and the period may last for four to eight days (1).
A period is termed irregular when it falls outside the average range for at least the last six months. You will notice that your periods are infrequent or very unpredictable. You will have irregular periods if:
- The time gap from period to period changes
- You bleed heavier or lighter than usual
- Length of your period varies to a great extent
Based on the above factors, irregular periods have been categorized into the following types (2):
- Polymenorrhea: The cycle is shorter than 21 days. Periods are heavier and painful in this case.
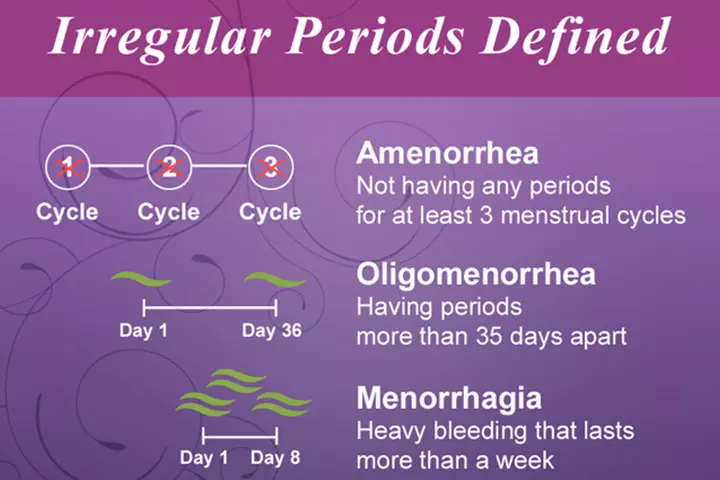
- Oligomenorrhea: The period cycle is longer than 35 days. You may have only four to nine periods in a year.
- Amenorrhea: It is the absence of menstrual periods for at least three consecutive period cycles or less than four periods in a year.
- Menorrhagia: It is the heavy or prolonged bleeding that lasts for more than a week or excessive bleeding occurring regularly.
Is It Normal To Have Irregular Periods?
It is normal to have irregular periods for the first few years of menstruation (around puberty), and as you near menopause (in the 40s) (3). An occasional irregular period is also normal unless it becomes frequent. You are the best to understand your cycle and notice if the period is irregular.
What Are The Reasons For Irregular Periods?
There are many possible causes of irregular periods. While some may be normal, some need medical attention. Hence you should consult a doctor to know the right cause for your irregular periods.
[ Read: PCOS And Pregnancy ]
Medical causes
- Pregnancy: It is one of the main reasons for missing your period. If you are sexually active and had unprotected intercourse, then a missed period could indicate pregnancy. Take a home pregnancy test a week after your missed period for confirmation.
- Breastfeeding: The prolactin hormone, which is responsible for stimulating breast milk, alters the reproductive hormones. This results in lighter or no periods but will become normal after stopping breastfeeding (4).
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS): Small cysts that develop on your ovaries alter hormonal levels and interfere with your periods. Some other signs of PCOS are excessive facial and body hair, baldness, acne, and obesity.
- Perimenopause: It is the phase that could occur several years before menopause, usually in the 40s. The body starts making less estrogen and the fluctuating estrogen levels make the period cycle longer or shorter. The other signs of perimenopause include night sweats, hot flashes, sleeping difficulties, mood changes, and vaginal dryness.
- Thyroid issues: Both overactive and underactive thyroid can cause irregular or late periods. The thyroid glands control metabolism that could affect the hormonal levels. In the case of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), you will have a shorter cycle and lighter periods along with weight loss, heart palpitations, and nervousness. In hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), you will have heavier periods, cramping, weight gain, and cold sensitivities.
- Uterine fibroids: These are non-cancerous muscular tumors which occur in the uterine wall. They lead to painful and heavy periods that could result in anemia. You will also have low back pain, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse and pain in the legs.
- Endometriosis: In this condition, the endometrial cells grow outside the uterine wall, and result in prolonged bleeding, heavy periods and bleeding between periods. You would also have painful bowel movements, gastrointestinal pain, and pain during intercourse (5).
- Contraceptives: Using birth control pills or intrauterine devices (IUDs) could cause irregular periods. Birth control pills could result in lighter periods (6) while IUDs cause heavier periods (7).
- Cervical and uterine cancers: They affect your period cycle, thereby causing heavier periods, or bleeding between periods. You will also have bleeding and unusual discharge during sex.
Lifestyle causes
- Stress: Stress at home, work and other areas of life could affect your menstrual cycle by interfering with the hormone production.
- Excessive exercise: Too much exercise and physical activities can affect the production of reproductive hormones and disturb the cycle.
- Weight gain or weight loss: Sudden changes in weight or eating disorders such as bulimia or anorexia could impact your period.
- Medications: Certain medications such as blood thinners, hormone replacement drugs, epilepsy drugs, thyroid medications, and antidepressants affect your periods.
- Travel: Travelling to different time zones, and going on long trips could affect your biological clock, and alter your menstrual cycle. Working in the nights and evenings can also affect the biological clock and your menstrual cycle (8).
If your irregular periods are due to lifestyle factors, then making changes in them could help you make the periods regular. However, medical causes need attention.
When To See A Doctor?
You need to see a doctor to understand the reason behind your irregular periods. Visit a doctor if:
- You have not gotten your periods for more than three months, and you are not pregnant.
- You had regular periods, but they suddenly turn irregular.
- Your period lasts longer than seven days and is heavy.
- Your period cycle is less than 21 days or more than 35 days long, and this is happening frequently.
- You are having severe bleeding and soaking one pad in an hour or two.
- You have severe and unbearable cramping.
- You often have spotting between periods.
- You have a fever or unusual discharge.
Your doctor will conduct specific medical examinations, including a pelvic exam and a Pap smear, to diagnose the right cause of irregular menstrual periods. The other tests include:
- Blood tests to check certain hormonal levels (follicle stimulating hormones, thyroid stimulating hormone, prolactin, cortisol, progesterone, and testosterone)
- Vaginal cultures to check for infections
- Pelvic ultrasound to check for ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids or polyps
- Endometrial biopsy and laparoscopy for diagnosing and treating certain conditions (such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory diseases, fibroids, ovarian cysts, some cancers)
The doctor may prescribe hormonal pills (such as oral contraceptives, progestin) or intrauterine devices (IUD) or suggest lifestyle changes to help balance your hormonal levels. Medical treatment depends on the cause of irregular periods.
[ Read: Endometrial Thickness ]
Home Remedies For Irregular Periods
While following the medical treatment prescribed by the doctor, you may also try some lifestyle changes and home remedies to bring your periods back on track.
Lifestyle measures:
- Have a healthy diet: If the irregularity is due to overweight or underweight, consult a nutritionist and get a diet plan. Include a healthy and balanced diet rich in nutrients and good fats, as they play a significant role in regulating periods.
- Exercise moderately: Over-exercise might affect your period adversely but moderate physical activity helps control weight gain and regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Practice yoga: Practicing yoga at least five times a week will regulate hormones and period cycle. It also reduces premenstrual symptoms. A research study found that 126 participants who did yoga for 35 to 40 minutes, five days a week for six months noticed hormonal regulation related to irregular periods (9).
Home remedies:
- Ginger: It is known to regularize periods by controlling heavy bleeding and painful cramps (10). Mix one teaspoon of ginger powder in a cup of water, boil for five minutes and add sugar if needed. Consume the mixture after your meal.
- Cinnamon: It regulates the period cycle and is known to be an effective treatment for PCOS (11). Add one teaspoon of cinnamon powder to one glass full of warm milk, and drink it every day.
- Apple cider vinegar: Take about a one-eighth cup of apple cider vinegar every day to restore menstruation in the case of PCOS. Since ACV has a bitter taste, you may dilute it in water and add one tablespoon of honey (12).
- Pineapple: It is known to regulate periods as it contains the enzyme bromelain that softens the uterine lining.
- Sesame seeds and jaggery: Sesame seeds contain lignans that control hormones. When mixed with jaggery, it has a warming effect and helps initiate the period. Dry roast a handful of sesame seeds, and blend them with one teaspoon of jaggery. Take it every day in the morning on an empty stomach a few days before the expected period date.
- Raw papaya: The potent emmenagogue regulates menstrual flow. It contracts the uterine muscle fibers and soothes uterine walls. You can have either papaya slices or juice every day until your periods are regulated. Do not take them during periods.
- Turmeric: The warming herb balances hormones and regulates the period cycle. It also stimulates periods. You can add a teaspoon of turmeric powder to a glass of milk and take it until your period flow starts (13).
- Fennel seeds: Its emmenagogue properties trigger the period flow (14). Soak two tablespoons of fennels seeds in a glass of water, and leave overnight. Strain the solution in the morning, and drink it every day a few days before your period.
- Mint and honey: This combination is a potent Ayurvedic remedy for irregular periods (15). Mix one teaspoon of dried mint powder with one teaspoon of honey, and consume it every day until you notice an improvement in your period cycle.
- Carrot juice: This excellent source of iron helps regulate the period cycle (16). Take a glass of carrot juice every day at least for three months. You can also mix it with other vegetable juices for additional nutrition.
There is no way to prevent most of these conditions that cause irregular periods. But you can reduce the effect and the risk of getting it again by making the lifestyle changes and following the treatment recommended by the doctor.
Track your menstrual cycle for about three consecutive months to understand the menstrual pattern. If there is something unusual, you can discuss it with your doctor.
How To Track Your Period?
You can use a calendar, a notebook or our period tracking apps to track your periods.
If you are tracking on a calendar or a book, note down the first day of your period, and keep marking the days you have periods until they stop. Continue this for a couple of months, and gradually it will help you foresee the period the following month. You can figure out the length of the cycle, and the length of the period.
[ Read: Reasons For Cramping Without Period ]
Irregular periods are normal and could happen at least once in your lifetime. You do not have to worry if it happens occasionally but cannot ignore if it is frequent. Visit a doctor, get the prescribed tests done, and follow the treatment. This will make you less worried about your period.
Have you ever experienced irregular periods? How did you address it? Share your experiences with us in the comments section below.
References
2. Donald E. Greydanus et al.; Menstrual disorders in the adolescent female; University of Kentucky (2012)
3. Perimenopause: Rocky road to menopause; Harvard Health Publishing
4. What causes menstrual irregularities; The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; NIH (2017)
5. Problem periods; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2014)
6. The Pill; University Health Service; University of Michigan
7. Intrauterine Device (IUD); University Health Service; University of Michigan
8. Christina C. Lawson et al.; Rotating shift work and menstrual cycle characteristics; NCBI
9. Rani M et al.; Impact of Yoga Nidra on menstrual abnormalities in females of reproductive age; J Altern Complement Med (2013)
10. Farzaneh Kashefi et al.; Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) on heavy menstrual bleeding: A placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial; Wiley Online Library
11. Daniel H. KorT and Roger A. Lobo; Preliminary evidence that cinnamon improves menstrual cyclicity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial; American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2014)
12. Wu D et al.; Intake of vinegar beverage is associated with restoration of ovulatory function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome; Tohoku J Exp Med (2013)
13. Sachin B.Somwanshi et al.; Women’s health issue: a brief overview on irregularities in menstruation; International Journal of Novel Research and Development (2017)
14. Arezoo Moini Jazani et al.; Herbal medicine for oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea: a systematic review of ancient and conventional medicine; BioMed Research International (2018)
15. Brittany Wood Nickerson; Recipes from the Herbalist’s Kitchen: Delicious, Nourishing Food for Lifelong Health and Well-Being
16. Acharya Vipul Rao; Herbal Cure for Common Diseases

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.