Concussion In Teens: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Guide
Persistent headaches, vision problems, and cognitive issues require prompt medical attention.

Image: iStock
In This Article
Vigorous outdoor activities or sports increase the probability of concussions in teens. A concussion is a type of brain injury that is caused due to a blow to the head. Such a severe mechanical shock to the brain causes harm to the nerves and blood vessels inside the brain tissue. These shock-induced structural and functional changes in the brain might temporarily lose brain function. Teens with a concussion need immediate medical attention, and it may take them over a month for complete recovery.

Read this post to learn more about the causes of concussions in teens and ways to manage brain injury.
A Typical Timeframe Of Recovery From Concussion
A concussion is a neuronal trauma and takes time to heal. Infants, children, and teens respond to medications well and get early and complete recovery at a growing age. The symptoms usually appear within minutes or hours; however, in some cases, it may take days for the symptoms to appear.
The typical recovery time for a concussion depends on the severity of the brain injury. It might take a few hours to weeks and even up to a month for recovery (1). In more severe cases, the timeline may prolong up to months.
Causes And Risk Factors For Concussion In Teenagers
A concussion generally happens due to head injuries, thereby hampering normal brain activities. Teenagers who participate in sports and outdoor activities are more prone to concussions than others. Besides sports injuries, the following are some common risk factors and causes of concussion among teenagers (2).
- Road accidents
- Bike riding accidents
- Physical abuse
- Trauma from falls
- Shockwaves from explosives
Signs And Symptoms Of Concussions
The signs and symptoms of concussion in teens may vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some of the common mild symptoms include (3).
- Raised bump or swelling on the affected area
- Headache
- Neck stiffness
- Confusion
- Temporary loss of consciousness
- Dizziness
- Blurred or double vision
- Balance problems
- Emotional symptoms such as irritability, depression, and sadness
- Forgetfulness
- Distraction
- Lethargy
Some of the symptoms that need immediate medical attention include
- Severe headache
- Seizures
- Prolonged loss of consciousness
- Blood or watery discharge from the nose or ears
- Several rounds of vomiting or projectile vomiting
- Wide-open pupil
- Slurred speech
- Numbness in limbs
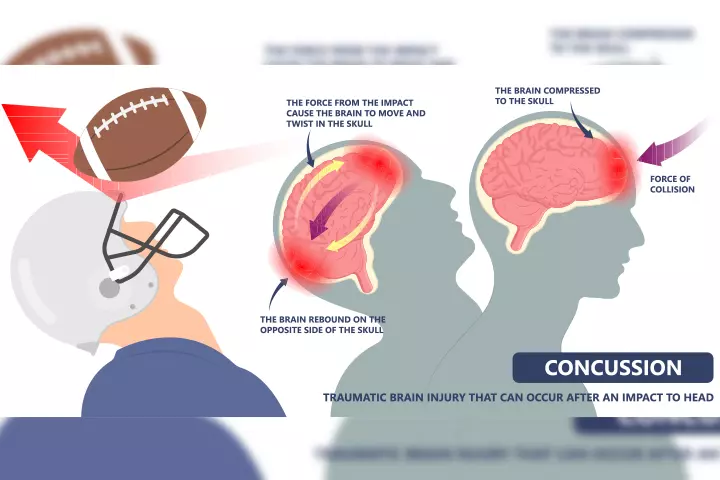
Biomechanics Of Brain Concussion
A head injury results in a chain of events at macroscopic and microscopic levels in the brain. The impact results in rapid pressure changes across the brain tissue.
The head impact may lead to brain tissue deformation. There may be structural damage such as rupture, blockage of blood vessels, and damage to the neurons, or functional damage such as changes in neurological status.
Thus, the symptoms of concussion start appearing within minutes or hours after a head injury (4) (5).
Complications Of Brain Concussion
A sports-related concussion is a delicate condition and may cause complications depending on the severity of the brain injury (3) (6).
- Post-concussion syndrome: The teen may experience persistent symptoms of brain concussion for weeks and months.
- Anxiety and depression: The teen may be at a higher risk of depression and anxiety disorders.
- Memory and language: The teen may find it challenging to recollect events, names, and words.
- Dementia and cognitive abilities: Concussion may increase the teen’s risk of dementia and affect their cognitive abilities.
- Vision and hearing: The patient may have difficulty seeing and hearing things post the concussion.
Diagnosis Of Concussion In Teens
A qualified medical doctor can carry out the diagnosis of the incidence of concussion. It is an excellent idea to shift the brain concussion patient to the nearest trauma center. A neurologist will monitor the teen’s condition by asking about their health history, family history, symptoms, the incidence of concussion, or recent head injury (7).
The doctor may also ask the teen questions pertaining to their
- Mental status, such as their mood and their ability to balance or do things independently.
- Sense of smell, hearing, vision, etc., to learn about any abnormalities associated with the cranial nerves. Motor functions and coordination.
Apart from these, the doctor may also order CT scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) if they suspect any severe effects of a concussion.
Treatment For Concussion In Teens
It is of paramount importance to identify and treat concussions at the earliest. Generally, teens with concussions may not require prolonged hospitalization and may recover well with at-home monitoring (8). The treatment may include any or a combination of these options (3)
- Rest: Physical rest and abstaining from demanding mental activity for several days or months.
- Routine: It is good to stay away from reading, writing, spending time on digital devices, and doing physical activities.
However, following a routine can help in the recovery process. As their condition improves, a gradual increase in the activities is recommended.
- Medications: Prescribe pain medications, such as acetaminophen, after consultation with a doctor.
- Diet: Due to brain injury, the patient may not feel hungry or thirsty. Caregivers should work out a balanced diet for the teen and ensure they are well fed and hydrated to maintain sugar and electrolyte balance in the blood.
Management Of Long-Term Concussion Issues
Management of long-term concussions aims at reducing the risk of getting further head injuries. This can be done by following a healthy lifestyle balance (3) (9).
- Adhering to the traffic rules by wearing a helmet or using a seat belt.
- Walking by holding the handrails and using walking aids.
- Maintaining a routine exercise schedule to strengthen core muscle strength.
- Using protective equipment during sports and other activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the long-term effects of a concussion?
The long-term effects of a concussion include (10):
- Changes in one’s personality
- Concentration problems
- Increased risk of psychological problems such as depression
- Sensitivity to loud noises or bright lights
- Absentmindedness
2. What happens if a concussion goes untreated?
If a concussion is left untreated, it might increase the risk of complications such as vertigo, consistent headaches, and dizziness.
Concussions are common in teens, especially those who take part in sports. Teens generally achieve complete recovery from concussions in a month. However, in cases of severe injury, they may need intensive medical care and undergo hospitalization for a prolonged period. A teen’s chance of recovery can be improved by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and reducing the risk of further brain injury.
Key Pointers
- Due to their growing age, teenagers who have concussions respond well to treatments and recover completely.
- Headache, neck stiffness, raised bump or swelling in the affected area, and confusion are some signs and symptoms of concussion.
References
- Recovery from Concussion.
https://www.cdc.gov/headsup/basics/concussion_recovery.html - Head Injuries.
https://www.stlouischildrens.org/conditions-treatments/head-injuries - Concussion.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15038-concussion#symptoms-and-causes - Neuroscience Biomechanics and Risks of Concussion in the Developing Brain.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK185339/ - Luke C Henry et al.; (2010); Neurometabolic changes in the acute phase after sports concussions correlate with symptom severity.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19761385/ - Complications – Severe head injury.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/severe-head-injury/complications/ - THE FIVE-MINUTE NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/neurosurgery/images/5-minute-neuro-exam-handout.pdf - Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI).
https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia/related_conditions/traumatic-brain-injury - Treatment and Management of Prolonged Symptoms and Post-Concussion Syndrome.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK185342/ - Concussions: How they can affect you now and later.
https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/postings/2016/11/concussion.php#:~:text=Long%20Term%20Effects%20of%20a%20Concussion&text=Trouble%20concentrating,Sensitivity%20to%20light%20and%20noise

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Neha Bhave Salankar