What Is Sun Damage? Can It Be Reversed?
Protect your skin from harmful rays and discover effective ways to restore its glow.

Image: Shutterstock
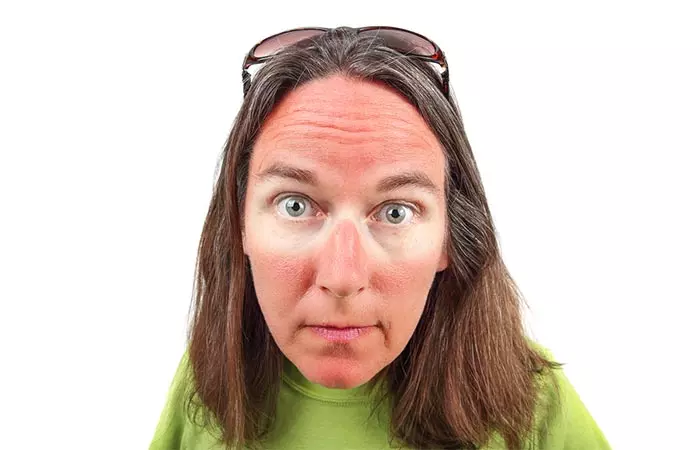
Who doesn’t love sunshine? You will hardly find anyone who doesn’t like to bask in the warm rays of the sun. But, too much of it can damage your skin in ways beyond your imagination. About 80% of the visible signs of aging – including wrinkles, scaling, roughness, and dryness – are a result of UV exposure. Sun rays can also cause pigmentation issues and cancer (1)! That’s a major concern. Sun damage cannot be completely reversed but can be managed and reduced. In this article, you will learn everything about sun-damaged skin and ways to treat it. Read on.

In This Article
How Do Sun Rays Damage Your Skin?
Exposure to solar UV radiations damages your skin. This damage can accumulate over your lifetime, only to show up later. In other words, the skin damage that you see today is a long-term effect of sun exposure.
Sunlight is comprised of:
- Visible light
- Infrared radiation
- Ultraviolet radiation
UV rays can be further broken down into three types:
- UVA Rays: They have a longer wavelength and can reach the deeper layers of your skin. UVA rays cause immediate tanning, damage the skin cells, and make them age faster. These rayscause wrinkles and fine lines. UVA also acts as a carcinogen (1).
- UVB Rays: These rays cause sunburn. They stimulate melanin production, causing delayed tanning. Along with UVA rays, UVB rays also contribute to skin aging and can cause skin cancer (1).
- UVC Rays: These rays are the most damaging. Thankfully, the ozone layer prevents them from reaching the earth’s surface.
People who have fairer skin are more susceptible to sun damage as their skin contains less melanin. However, this does not mean people with dark and olive complexions are safe. Their skin may be less sensitive to the sun, but unprotected UV exposure can take a toll on them as well. In the next section, we will discuss the problems caused by sun exposure.
Types And Signs Of Sun-Damaged Skin
The most common types of sun damage include:
1. Sunburn
What Is It?
Sunburn is a painful skin condition caused by overexposure to UV radiation. It is a type of radiation burn that affects your skin cells. Sunburn is your body’s inflammatory response when the UV rays cause DNA damage. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, UVB rays cause sunburn and change the molecular structure of your DNA (2), (3).
Signs And Symptoms
- Redness
- Pain
- Swelling
- Blisters
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Fever
The last four are symptoms of severe sunburn.
How To Treat
- Apply cold compress.
- Avoid touching the blisters.
- Apply over-the-counter medicines.
- Keep the skin moisturized.
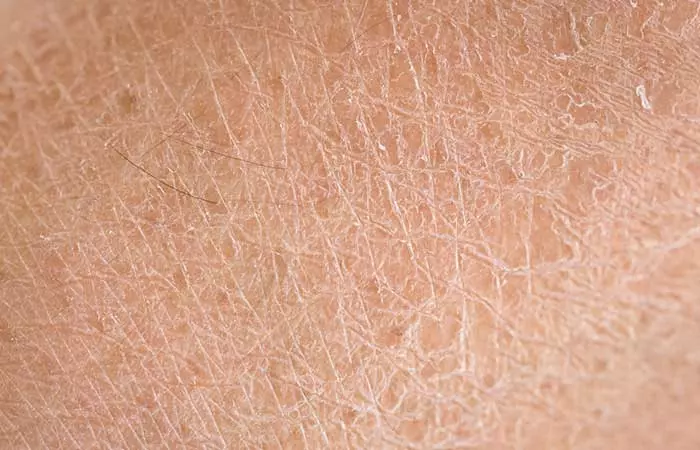
2. Dry Skin
What Is It?
Your skin becomes dry when it lacks moisture. UV rays can dry out your skin and cause scaling and irritation.
Signs And Symptoms
- Flaking
- Scaling
- Ashy skin
- Redness
- Itching
- Roughness
How To Treat
- Exfoliate with a loofah.
- Moisturize your skin.
- Apply petroleum jelly (avoid this if you are experiencing sunburn as well).
- Drink plenty of water.
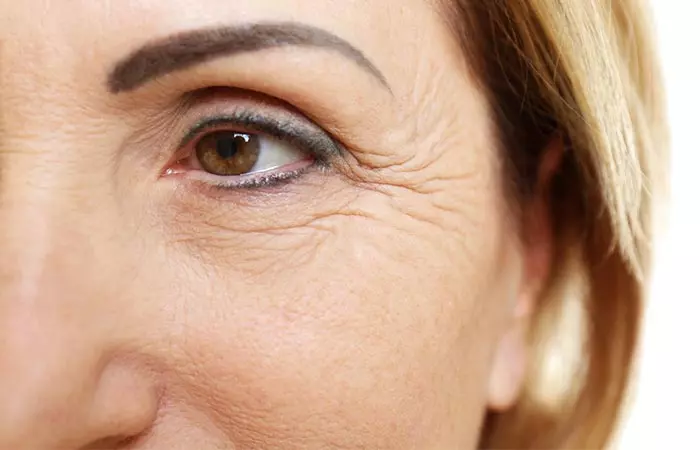
3. Wrinkles And Fine Lines
What Is It?
Overexposure to the UV rays can deactivate the carotenoids in your skin that protect it from oxidation. However, when the carotenoids are deactivated, the dermal collagen and elastin that keep your skin tight and smooth are degraded (1). As a result, you get wrinkles and fine lines.
Signs And Symptoms
- Lines and creases on your skin that are especially noticeable around your eyes, neck, and mouth area.
How To Treat
Consult a dermatologist to devise skincare plan to combat fine lines and wrinkles. The dermatologist may suggest anti-wrinkle treatments, such as:
- Topical retinoids
- Beta-carotene supplements
- Chemical peels
- Laser therapy
- Microdermabrasion
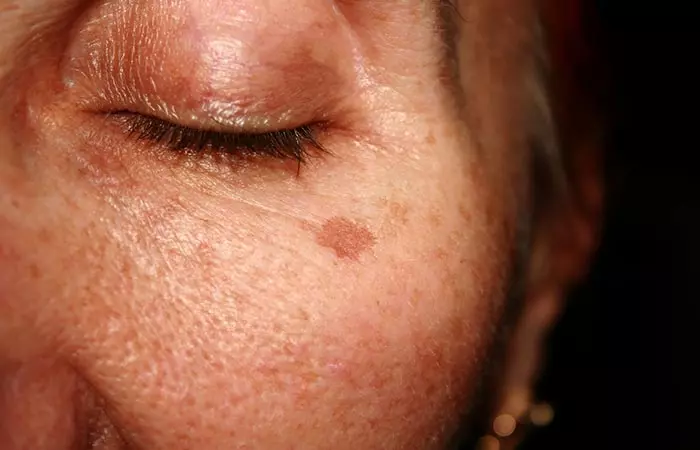
4. Age Spots
What Is It?
Also known as solar lentiginosis or solar lentigo, these are dark patches on the skin caused by overexposure to UV rays, which makes the melanin clump in your keratinocytes (skin cells).
Signs And Symptoms
Flat and oval dark spots and pigments that:
- appear on face, feet, upper back, and shoulders
- are usually brown, black, or tan
How To Treat
The dermatologist may prescribe:
- Skin lightening creams containing glycolic and kojic acids and hydroquinone
- Retinoids
- Chemical peel
- Laser therapy
- Microdermabrasion
- Cryotherapy
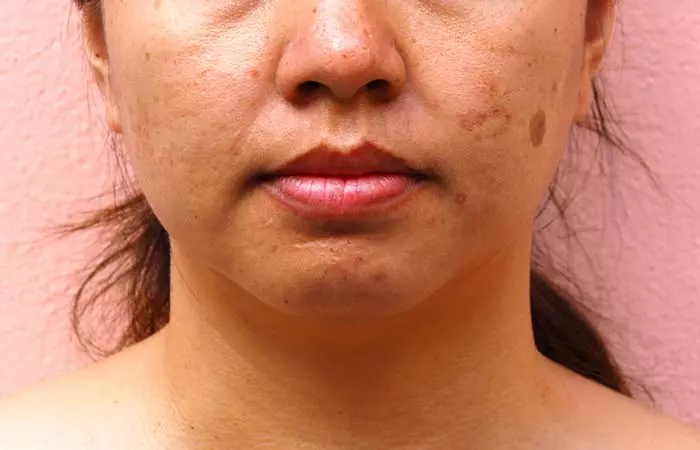
5. Melasma
What Is It?
Melasma is a condition characterized by dark brown or gray patches on your skin. The exact cause of melasma is not yet known, but sun exposure can trigger melanin production that creates these spots on the skin. However, there are other factors that may cause overproduction of melanin and result in melasma.
Signs And Symptoms
Dark patches that often appear on:
- Forehead
- Bridge of your nose
- Cheeks
- Chin
- Forearms
- Neck
How To Treat
The dermatologist may prescribe:
- Skin lightening creams (topical steroids)
- Dermabrasion
- Chemical peels
- Microdermabrasion
- Minimize sun exposure
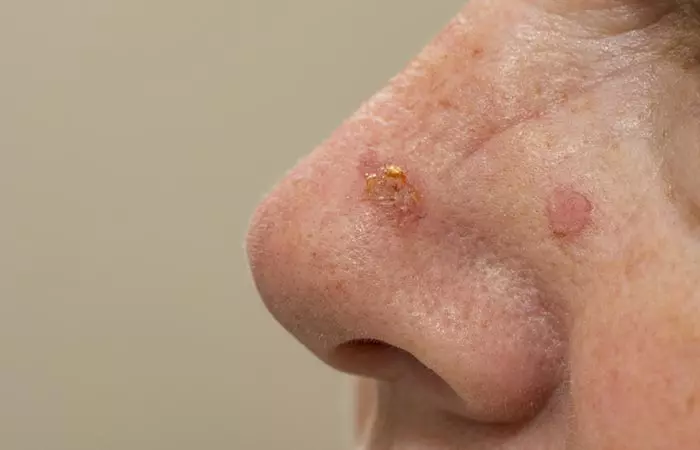
6. Actinic Keratosis
What Is It?
This condition is also known as Solar Keratosis. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, it is a crusty and scaly growth caused by UV ray exposure. It is the most common type of precancerous lesion and, if not treated, can develop into skin cancer (4).
Signs And Symptoms
- Slightly raised bump or patch on the skin that is rough, dry, and scaly
- Sometimes, the bump has a wart-like surface.
- Is pink, red, or brown
- Burning and itching sensation in the area
How To Treat
The dermatologist may prescribe:
- Surgical procedures, such as laser therapy or cryosurgery
- Topical treatments, such as 5-fluorouracil (topical chemotherapy), Imiquimod (to kill precancerous cells), and chemical peel
- Photodynamic therapy
Prevention is the key to avoiding sun damage. However, if your skin does get damaged, keep in mind that the effects are often long-term. While it is not possible to completely reverse the damage caused by UV exposure, you can reduce it to a certain extent. In the next section, find out how to prevent and mitigate the adverse effects of sun exposure.
Sun Survival Tips: How To Prevent And Reverse Sun Damage
Sun damage can be easily avoided. You need to practice proper sun protection throughout the year to prevent the negative effects of sun exposure. Here is what you can do to prevent and reverse the effects:
1. Never Say ‘No’ To Sunscreen
This is a thumb rule you should never forget. Remember that the UV rays reach the earth’s surface even on cloudy and rainy days. So, cover up with sunscreen. Always use a sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
2. Exfoliate Your Skin
Dead skin cells accumulate on the outmost layer of your skin, making it rough, blotchy, and uneven. Moreover, remnants of the makeup and skin care products you put on your face make it look dull and dirty. Exfoliation gets rid of all the dead skin cells and traces of makeup, making your skin appear brighter.
3. Try Bleaching
Bleaching helps lighten dark spots and pigmentation. Before trying out OTC bleaching agents, it is best to consult a dermatologist and use products recommended by them. The dermatologist may recommend products containing retinol, kojic acid, and hydroquinone. These ingredients help lighten stubborn discoloration and patches.
4. Keep Your Skin Moisturized
Excessive exposure to sun rays, salt water, and chlorine (in swimming pools) can dehydrate your skin. To prevent that, use good quality body, hand, and foot creams. Use products that contain hyaluronic acid. It replenishes your skin and reduces the appearance of wrinkles. Continued moisturization may also boost collagen production and improve your skin texture.
5. Try LED Light Therapy
LED therapy uses lights of different wavelengths – including red and blue lights – reduce fine lines and wrinkles and boost collagen production. Talk to a dermatologist before buying any LED light therapy device and using it on your skin. You can also visit a dermatologist and get it done under professional supervision.
6. Be Aware Of Medications And Skin care Products
Some medicines and skin care products may increase your sun sensitivity and the risk of UV damage. They include prescription medication (antibiotics such as tetracyclines and antidepressants) and skin care ingredients, such as AHAs and BHAs, retinol, and essential oils. If you are using any such medication or skin care products, consult a doctor to find out the special precautions you need to take to avoid sun damage.
7. Use Skin Care Ingredients To Reverse The Effects Of Sun Damage
Potent skin care ingredients, such as niacinamide, retinol, retinoids, azelaic acid, AHAs, BHAs, and vitamin C, can help reduce and improve the effects of sun damage. These ingredients can reduce hyperpigmentation, fine lines, dark spots, and wrinkles to enhance the appearance of your skin. However, the concentration of the ingredients depends on the extent of damage and the tolerance level of your skin. So, talk to a doctor to determine the type and concentration of ingredients your skin needs.
“Prevention is better than cure” sounds like an overused phrase. But when it comes to sun damage, prevention is easier than reversal. Preventing sun damage is not an arduous task. You need to ensure that you:
- Avoid going out in the sun during the peak hours (between 10 am and 4 pm).
- Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and hats.
- Using broad-spectrum SPF protection.
Make these simple tips a habit before your sun damage become unmanageable. If you have any more questions about this skin problem, drop them in the comments section below, and we will get back to you.
References
Articles on thebridalbox are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Ultraviolet Radiation, Aging and the Skin..”, Molecules, US National Library of Medicine
- “UVA & UVB”, Skin Cancer Foundation
- “Molecular Mechanisms of Ultraviolet..”, Journal of Nucleic Acid, US National Library of Medicine
- “Actinic Keratosis”, Skin Cancer Foundation

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha