Serious Side Effects of Tea Tree Oil: Risks, Reactions, and Precautions
Explore side effects of tea tree oil, including skin reactions, toxicity, hormonal impacts, and safety tips for healthy use.
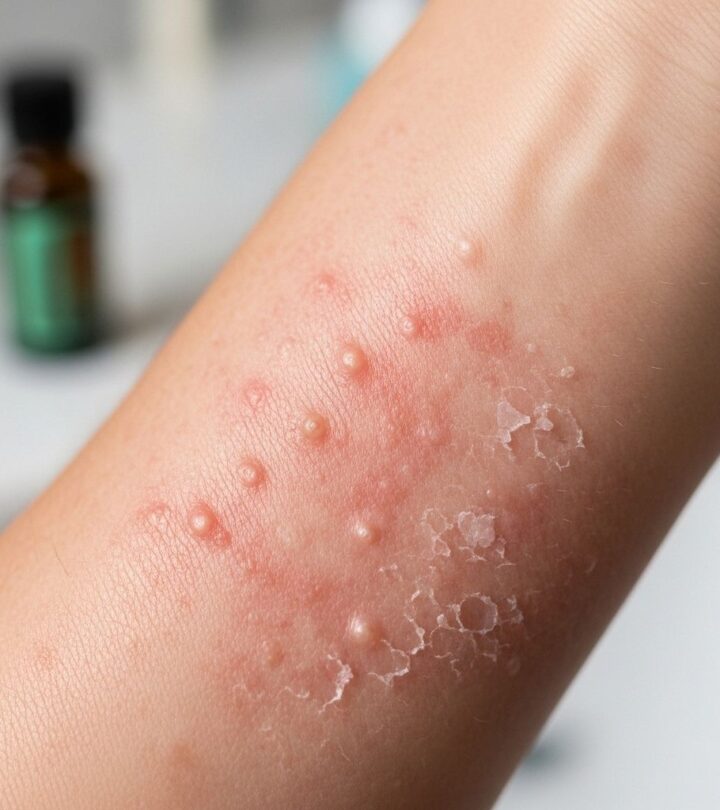
Image: ShutterStock
Serious Side Effects of Tea Tree Oil: What You Need to Know
Tea tree oil, derived from the leaves of Melaleuca alternifolia (the Australian tea tree), is a popular essential oil known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Used in remedies for skin complaints, respiratory symptoms, and household cleaning, tea tree oil may offer several benefits. However, improper use or individual sensitivity can lead to serious side effects, some of which are potentially severe. This article explores the risks, reactions, scientific evidence, and guidance you need to use tea tree oil safely.
What Is Tea Tree Oil?
Tea tree oil is an essential oil traditionally used as an herbal medicine and antiseptic by the Aboriginal People of Australia. Today, it is promoted for treating:
- Skin conditions (acne, athlete’s foot, dandruff)
- Head lice and scabies
- Cuts, burns, and insect bites
- Respiratory ailments (cough, congestion)
- Included in shampoos, lotions, soaps, and cleaning products
Despite its popularity, scientific support for many of these uses remains limited, and inappropriate application can result in harmful effects.
Common Side Effects of Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is considered safe for most people when used topically in small amounts and in diluted preparations. Nonetheless, several adverse effects have been documented:
Skin Reactions and Allergies
- Irritation: Redness, burning, stinging, itching, and scaling may occur, especially when using undiluted oil or on sensitive skin.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Characterized by rash, hypersensitivity, and redness. This may be unpredictable and often occurs when the oil is old, degraded by light or air, or applied in large amounts.
- Worsening of Skin Conditions: Those with eczema, psoriasis, or other autoimmune-related skin issues are more susceptible to adverse skin reactions.
- Eye Damage: Tea tree oil must never be applied near or to the eyes as it can cause corneal damage.
Respiratory Irritation
- Inhalation of tea tree oil vapors can induce coughing, nose and throat irritation, and shortness of breath in sensitive individuals.
- People with pre-existing conditions like asthma should consult a doctor before using tea tree oil aromatically.
Hormonal Effects
- Rare cases have documented gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement) in boys and premature breast formation in girls after topical exposure to tea tree and lavender oils. These effects reversed after discontinuation.
- The exact mechanism is unclear, and the unregulated nature of over-the-counter products raises concerns about unknown concentrations and contaminants.
Toxicity: Why Ingestion Is Dangerous
Tea tree oil is highly toxic if ingested, with potential life-threatening consequences even in small amounts. It should never be swallowed by humans or animals, despite some mistaken traditional practices. Documented cases include:
| Age | Amount | Symptoms | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 years | Small | Coma | Recovered |
| 23 months | 10mL | Confusion, lost ability to walk | Recovered in 5 hours |
Swallowing tea tree oil can cause symptoms such as:
- Central nervous system depression
- Disorientation and ataxia (loss of muscle coordination)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Coma
- Lung tissue damage (if aspirated)
If accidental ingestion occurs, seek medical attention or call Poison Control immediately. Do not wait for symptoms to appear, as poisoning can develop within minutes.
Risks for Sensitive Groups
- Children: More susceptible to toxicity due to their lower body weight. Even minor amounts can cause severe adverse symptoms.
- Pregnant/Breastfeeding Women: Lack of safety data suggests these groups should avoid tea tree oil.
- People with Hormonal Issues: Rare hormonal effects have been documented; caution is advised.
- Individuals with Respiratory Disorders: Increased risk of inhalation side effects; consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Those with Sensitive Skin: Higher risk of allergic and irritant reactions. Always patch test before regular use.
Tea Tree Oil Poisoning in Pets
Tea tree oil is toxic to animals, particularly cats and dogs, whether ingested or applied topically. Poisoning symptoms in pets include:
- Increased drooling
- Extreme fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Tremors
- Uncoordinated movement (ataxia)
Pets exposed to tea tree oil may require veterinary care for recovery. Never use tea tree oil on or around pets unless specifically instructed by a veterinarian.
Scientific Evidence and Adverse Reaction Reports
Tea tree oil’s popularity has driven significant case reporting:
- In 2022, Poison Control centers managed over 2200 cases of human exposure to tea tree oil—more than any other named essential oil.
- More than 10% required treatment at healthcare facilities due to severity of symptoms.
- The World Health Organization received 159 reports of adverse skin reactions from tea tree oil use, including rashes and hypersensitivity.
The range of product quality and concentration available on the market may influence both efficacy and the risk of side effects.
Who Should Avoid Tea Tree Oil?
Certain groups should avoid tea tree oil due to increased risk of adverse effects:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Infants and young children
- Individuals with a history of skin allergies or hypersensitivity
- Those with hormonal disorders
- People with asthma or respiratory ailments
- Pet owners (never apply to or near animals)
Always consult a healthcare professional if considering tea tree oil for medicinal or home use in these groups.
Safe Use and Prevention Tips
To minimize risks, follow these safety guidelines:
- Patch Test: Always conduct a skin patch test before extensive use.
- Dilution: Use tea tree oil only when diluted in carriers, such as coconut or olive oil. Avoid undiluted application.
- Storage: Keep tea tree oil in dark, airtight bottles away from light and air, as exposure can increase skin reaction risk.
- Avoid Sensitive Areas: Never apply tea tree oil near the eyes, mouth, or on broken skin.
- Keep Out of Reach: Store tea tree oil away from children and pets.
- Do Not Ingest: Never swallow tea tree oil. It is strictly for topical or external use only.
- Discontinue Use: Stop immediately if you experience rash, redness, itching, swelling, or other unusual reactions.
When to Seek Medical Care
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience or observe:
- Severe skin rash or blistering
- Difficulty breathing, coughing, or throat irritation after inhaling vapors
- Confusion, uncoordinated movements, or seizures (especially in children or after ingestion)
- Animal exposure resulting in drooling, lethargy, or tremors
Contact Poison Control or a healthcare provider for advice and rapid intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I use tea tree oil directly on my skin?
It is not recommended to use undiluted tea tree oil directly on the skin, as this increases the risk of irritation and allergic reactions. Always dilute before application and conduct a patch test first.
Q: Is it safe to consume tea tree oil?
No. Tea tree oil is toxic when ingested and can lead to serious, life-threatening symptoms. It should only be used externally and never swallowed.
Q: Are there any long-term side effects from using tea tree oil?
No chronic long-term effects are well documented, but repeated skin exposure may result in persistent irritation or sensitization in sensitive individuals. Hormonal effects, such as temporary breast tissue changes in children, have reversed after stopping exposure.
Q: Can I use tea tree oil around my pets?
No. Tea tree oil is highly toxic to cats and dogs, both if applied to their skin or ingested. Seek veterinary advice before using any essential oils around animals.
Q: Who should avoid tea tree oil?
Pregnant or lactating women, young children, people with asthma or sensitive skin, those with hormonal disorders, and pet owners should exercise particular caution or avoid using tea tree oil altogether.
Q: What should I do if someone accidentally ingests tea tree oil?
Immediately call Poison Control or visit the emergency department. Do not wait for symptoms to appear, as tea tree oil can cause dangerous poisoning within minutes.
Quick Reference Table: Risks By Application
| Method | Potential Side Effects | Recommended Precaution |
|---|---|---|
| Topical (skin) | Irritation, contact dermatitis, allergy, hormonal effects | Patch test; dilute; avoid sensitive areas; discontinue on reaction |
| Inhalation | Respiratory irritation, coughing | Limit exposure; avoid in asthma/respiratory disorders |
| Ingestion | Toxicity (CNS depression, coma, vomiting) | Never ingest; seek immediate medical care if swallowed |
| Application to pets | Drooling, fatigue, ataxia, death | Do not use on or around animals |
Final Thoughts
Tea tree oil is a potent natural remedy with both therapeutic promise and real risks. Awareness of side effects, proper use, and prompt action during adverse reactions can help ensure safe enjoyment of its benefits. For any question regarding its suitability, consult with a healthcare professional.
Recommended Readings
- “Tea Tree Oil Side Effects: On Your Skin and Inhalation” – Healthline
- “Tea Tree Oil: Remedy and Poison” – Poison Control
- “Safety assessment and adverse drug reaction reporting of tea tree oil” – PubMed
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/tea-tree-oil-side-effects
- https://www.poison.org/articles/tea-tree-oil
- https://www.icicilombard.com/blogs/health-insurance/mb/tea-tree-oil-side-effects
- https://www.lareb.nl/en/news/side-effects-of-tea-tree-oil/
- https://www.mskcc.org/pdf/cancer-care/patient-education/herbs/tea-tree-oil?mode=large
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36420525/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.7687
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/262944
Read full bio of Medha Deb