Serious Side Effects of Barley Water: Risks, Precautions, and Health Considerations
Learn about the hidden risks associated with barley water and who should avoid this seemingly healthy drink.
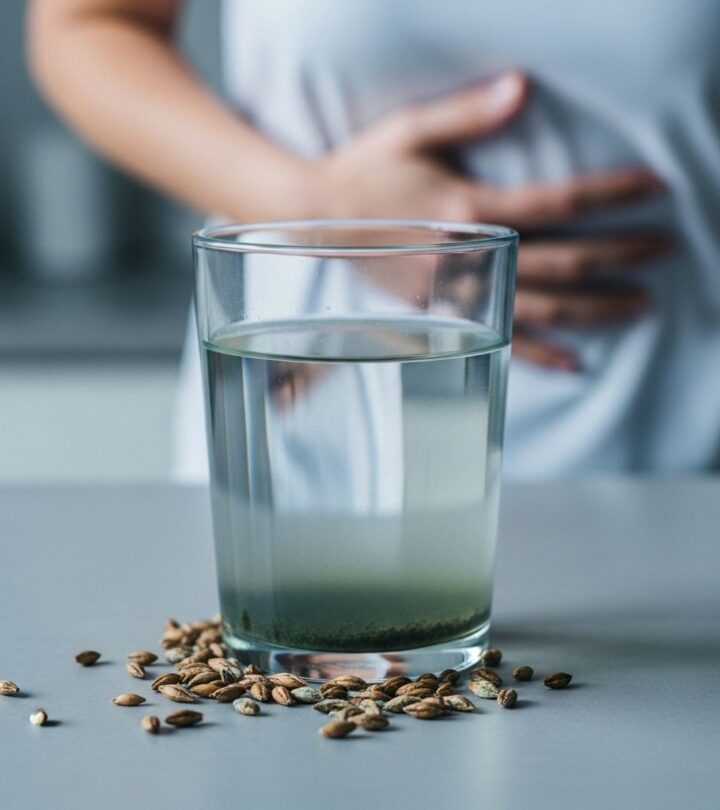

Image: ShutterStock
Serious Side Effects of Barley Water
Barley water is a traditional drink often portrayed as a health tonic. While it indeed offers several benefits, it also carries risks that may outweigh its advantages for certain individuals. Below, we comprehensively explore the side effects, precautions, and conditions under which barley water may not be suitable for consumption.
What Is Barley Water?
Barley water is made by boiling barley grains in water and straining the liquid. It is consumed worldwide for its supposed ability to aid digestion, promote detoxification, and support kidney health. However, like many health drinks, it is important to examine any side effects before incorporating it regularly into your diet.
Potential Side Effects of Barley Water
While many people can consume barley water safely, there are several notable side effects that should be considered, particularly for those with existing health concerns.
- Digestive discomfort
Unstrained barley water is packed with fiber which, while beneficial for most, can cause stomach cramps, bloating, flatulence, constipation, or a sensation of fullness when consumed in excess. Some individuals report nausea, rashes, headaches, vomiting, and diarrhea after intake—especially if they have sensitive digestive systems. - Allergic reactions
Barley contains gluten and is a common culprit for allergic reactions. Those with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, or allergies to other cereal grains (such as wheat, rye, oats, corn, or rice) may experience symptoms including skin rashes, abdominal pain, or respiratory issues. - Risk of weight gain
Unsweetened barley water is not typically high-calorie, but adding sweeteners or fruit juices can increase its energy content substantially, possibly leading to unintended weight gain if consumed in large quantities. - Drug interactions and blood sugar effects
Barley water can lower blood sugar levels, which poses a risk for those taking diabetes medications or preparing for surgery. Drinking barley water may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, requiring medication adjustments. - Electrolyte Imbalance
Excessive intake of barley water may disrupt electrolyte balance, particularly since it acts as a diuretic and increases urination. This can strain kidney function and is concerning for people with renal disease. - Asthma Trigger
Although rare, barley flour and its derivatives may trigger asthma in sensitive individuals. - Acrylamide Content in Barley Tea
Barley tea, made from roasted barley, may contain small amounts of acrylamide—a potentially carcinogenic compound. Research on acrylamide’s health impacts is mixed, so the risk may be minimal, but people concerned about cancer risk should be aware. - Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Barley is considered likely safe when eaten in normal food quantities during pregnancy. However, barley sprouts or excessive barley consumption may pose risks; there isn’t enough reliable data about its safety during breastfeeding.
Who Should Avoid Barley Water?
The following groups should be especially cautious or avoid barley water altogether:
- Individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease
Barley is a rich source of gluten and can severely exacerbate symptoms in affected individuals. - People with cereal grain allergies
Cross-sensitivity to barley is common among those allergic to other grains. - Diabetics
Regular barley water intake may lead to unpredictable drops in blood sugar, especially if you’re on medication. - Renal Patients
Its diuretic nature can put a strain on kidneys and disrupt electrolyte balance. Kidney patients should also avoid the addition of lemon peel, which is sometimes added for flavor. - Pregnant or breastfeeding women
Moderate food-based consumption is considered safe, but barley sprouts and supplements lack sufficient safety data. - People scheduled for surgery
Barley’s blood sugar lowering properties may interfere with perioperative management; discontinue at least two weeks before surgery.
Common Symptoms of Side Effects
Symptoms vary depending on individual sensitivity, underlying health conditions, and the amount consumed. Common symptoms include:
- Bloating and gas
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Stomach cramps and indigestion
- Rashes, skin irritation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches
Ways to Minimize or Prevent Barley Water Side Effects
If you wish to consume barley water but have concerns about side effects, consider these precautions:
- Begin with small amounts and gradually increase intake to monitor your body’s response.
- Choose pure barley water without added sugars, sweeteners, or juices to avoid extra calories and retain health benefits.
- Strain barley water thoroughly to remove grains and reduce excess fiber that can cause digestive issues.
- Limit barley water intake to 1–2 cups per day. Excessive amounts can lead to digestive and metabolic imbalances.
- Consult your doctor or nutritionist before adding barley water to your diet, especially if you have chronic health conditions.
- If you have kidney issues, monitor electrolyte levels and avoid diuretic drinks without medical supervision.
- If consuming barley tea, opt for deeply roasted barley, which may have lower acrylamide content.
Table: Frequent Side Effects and At-Risk Groups
| Side Effect | At-Risk Group | Precaution |
|---|---|---|
| Digestive upset (bloating, cramps, gas) | Sensitive digestive systems, high fiber intake | Strain properly, reduce quantity |
| Gluten allergy/celiac symptoms | Gluten intolerant, celiac, grain-allergic | Avoid barley water completely |
| Blood sugar fluctuations | Diabetics, perioperative patients | Consult doctor; stop before surgery |
| Electrolyte imbalance | Renal patients, frequent consumers | Limit intake; consult nephrologist |
| Asthma | Asthmatics, grain-allergic | Observe symptoms, avoid if triggered |
| Potential cancer risk (acrylamide in tea) | Regular barley tea drinkers | Dark roast barley before preparation |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can barley water be consumed daily?
In moderation, barley water is safe for most individuals. It is recommended to limit intake to 1–2 cups per day and monitor for any adverse reactions.
Q2. Does barley water aid weight loss?
Barley water’s rich fiber content can promote satiety, potentially aiding weight loss, provided it is not consumed with high-calorie additives.
Q3. Is barley water gluten-free?
No. Barley water contains gluten and is unsuitable for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Q4. What is barley tea and does it have similar side effects?
Barley tea is a drink made by roasting barley and steeping it in water. It shares similar side effects to barley water, including gluten content and digestive concerns. It may also contain acrylamide, a compound under investigation for cancer risk.
Q5. Who should consult a doctor before using barley water?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, diabetics, those with kidney issues, and people with known grain allergies should seek medical advice before regular consumption.
Best Practices for Consumption
- Consult your doctor before adding barley water to your diet if you have any health conditions.
- Consume in moderation—usually 1–2 cups per day is sufficient for health benefits without side effects.
- Strain thoroughly to remove grain pieces and excess fiber.
- Opt for unsweetened or lightly sweetened versions to keep calorie content low.
- Avoid if allergic or sensitive to gluten or other cereal grains.
- Monitor for symptoms after initial consumption, especially digestive discomfort or allergic reactions, and adjust intake accordingly.
Conclusion: Stay Informed and Consume Responsibly
Barley water is a drink with many touted benefits but also significant risks for certain individuals. Recognizing the potential adverse effects—ranging from digestive issues and allergies to drug interactions and metabolic disturbances—is crucial for safe and responsible consumption. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, especially those related to gluten sensitivity, kidneys, diabetes, or pregnancy, should exercise caution and seek medical advice before consumption.
References
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/barley-health-benefits
- https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/barley-water-benefits-side-effects-&-its-recipe/1425
- https://www.metropolisindia.com/blog/preventive-healthcare/barley-water-benefits
- https://www.rxlist.com/supplements/barley.htm
- https://www.lybrate.com/topic/benefits-of-barley-and-its-side-effects
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/barley-tea-nutrition-benefits-and-side-effects
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9niYDWlzIeQ
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321577
Read full bio of Sneha Tete