Semolina: Nutrition, Health Benefits, Side Effects, and Uses
Uncover the nutritional value, health benefits, potential side effects, and versatile culinary uses of semolina flour.
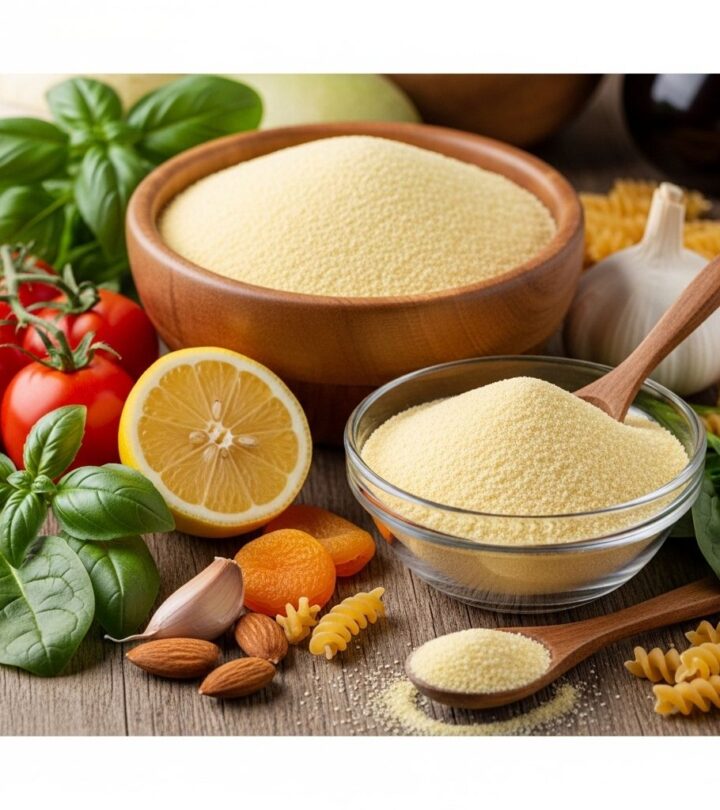

Image: ShutterStock
Semolina, derived from the coarse grains of durum wheat, is a popular flour used in numerous global cuisines. Recognized for its unique texture and subtle flavor, semolina is valued not just for its culinary applications, but also for its impressive nutritional profile and associated health benefits. This article explores everything you need to know about semolina, including what it is, its nutritional facts, health advantages, possible side effects, uses, and answers to frequently asked questions.
What Is Semolina?
Semolina is a granular flour milled from durum wheat, giving it a pale yellow color and distinctive slightly grainy texture. While best known as the primary ingredient in pasta, semolina is widely used for desserts, porridge, breads, and even savory dishes in Indian, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and European cuisines. Due to its relatively high gluten content, semolina imparts structure and firmness to recipes compared to all-purpose flour.
Semolina vs. Regular Flour
| Characteristic | Semolina | All-Purpose Flour |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Durum wheat | Common wheat |
| Texture | Coarse, gritty | Fine, soft |
| Color | Pale yellow | White |
| Gluten content | High | Moderate |
| Culinary uses | Pasta, upma, puddings, couscous | Pastries, bread, cakes |
Nutritional Value of Semolina
Semolina is packed with essential nutrients, making it a superior choice for health-conscious individuals. The following nutritional facts are based on a standard 56-gram (about 1/3 cup) uncooked serving of enriched semolina:
- Calories: 198
- Carbohydrates: 40 g
- Protein: 7 g
- Fat: Less than 1 g
- Fiber: 2 g (7% of the recommended daily intake)
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): 41% of RDI
- Folate (Vitamin B9): 36% of RDI
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): 29% of RDI
- Iron: 13% of RDI
- Magnesium: 8% of RDI
- Other minerals: Contains phosphorus, calcium, potassium, zinc, and selenium
These nutrients collectively support key bodily functions, including energy production, red blood cell formation, metabolism, and immune defense.
Health Benefits of Semolina
When consumed as part of a balanced diet, semolina offers a wide array of health benefits. Here are the most significant ones:
1. Provides Sustained Energy
The complex carbohydrates in semolina are digested slowly, ensuring a steady release of energy throughout the day. This quality makes it ideal for breakfast dishes or mid-day meals, helping to prevent sudden energy slumps.
2. Supports Weight Management
Semolina’s high protein and fiber content promotes satiety, curbing the urge to overeat. When cooked with minimal fat and sugar, it becomes a beneficial food for those monitoring their weight.
- Low in fat
- Promotes feeling of fullness
- Helps maintain muscle mass during weight loss
3. Enhances Digestive Health
The dietary fiber in semolina aids in regular bowel movements and promotes gut health by nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. This can help reduce problems like constipation and support overall digestion.
4. Improves Heart Health
Being low in cholesterol and saturated fats, semolina is heart-friendly. It contains magnesium, selenium, and folate, all of which play a role in maintaining optimal cardiovascular function by regulating blood pressure, lowering bad cholesterol, and preventing oxidative stress.
5. Rich in Antioxidants
Selenium in semolina acts as a powerful antioxidant, defending the body from damage caused by free radicals. This reduces inflammation and lowers the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
6. Strengthens Bones
With minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium, semolina contributes to strong and healthy bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis with regular consumption.
7. Boosts Immunity and Energy
Zinc, selenium, and B vitamins collectively enhance immune response. The slow-releasing energy from semolina’s complex carbohydrates helps maintain high energy levels, combating fatigue through the day.
8. Promotes Brain and Nervous System Health
Rich in thiamine and folate, semolina supports cognitive health and may improve mental clarity, focus, and memory. Minerals such as magnesium and zinc also aid in nervous system functioning.
9. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
The slow-digesting carbs and magnesium content can help in stabilizing blood sugar, making semolina suitable for those with diabetes when eaten in moderation and alongside other low-GI foods.
10. Supports Muscle Growth and Recovery
Semolina is a moderate source of plant-based protein, which is necessary for building and repairing muscle tissue. Including it as part of post-workout meals can aid muscle recovery.
11. Stimulates Lactation
Traditionally used in postpartum diets, semolina is believed to promote lactation in new mothers due to its ability to stimulate the hormone prolactin, especially when cooked with ghee and jaggery.
How to Use Semolina in Cooking
Semolina’s versatility extends to both sweet and savory preparations. Here are some popular ways to use semolina in the kitchen:
- Pasta and Couscous: Main ingredient for traditional Italian pasta and North African couscous
- Desserts: Key ingredient in puddings like halwa or sheera, and Mediterranean pastries
- Breakfast Dishes: Used to make semolina porridge, Indian upma, and pancakes
- Baked Goods: Adds crispness to bread crusts, pizza bases, and cookies
- Coating: Used as a crunchy coating for pan-frying and baking dishes
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
While semolina is nutritious for most people, certain individuals should exercise caution.
- Gluten Content: Semolina contains a high amount of gluten, making it unsuitable for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
- Allergic Reactions: Some may experience wheat allergy symptoms, such as hives, rashes, or digestive discomfort.
- Caloric Density: Although not high in fat, semolina-based dishes can be calorie-dense, particularly when prepared with excess fat or sugar.
- Blood Sugar: Those with diabetes should monitor portion sizes and combine semolina with fiber-rich foods to avoid blood sugar spikes.
Semolina vs. Other Flours
| Flour Type | Protein (g per 100g) | Fiber (g per 100g) | Main Uses | Gluten Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semolina | 12-13 | ~3-4 | Pasta, upma, pudding | High |
| All-Purpose | 10-11 | ~2 | Baking, thickening | Moderate |
| Whole Wheat | 13-14 | ~11 | Breads, chapati | High |
| Rice Flour | ~6-7 | ~2 | Gluten-free Baking | None |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is semolina gluten-free?
No, semolina is made from durum wheat and contains gluten. It is not safe for those with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
Q: Can semolina help in weight loss?
Semolina can aid weight management due to its protein and fiber content, which help promote satiety. However, results depend on preparation methods and overall dietary habits.
Q: What dishes can I make with semolina?
Semolina is versatile; use it for pasta, couscous, puddings (halwa), Indian dishes (upma), baked goods, and as a crispy coating in casseroles and savory snacks.
Q: Is semolina suitable for diabetics?
Semolina digests slowly and contains magnesium, which may aid blood sugar control. Diabetics should consume it in moderation and combine with low-glycemic foods.
Q: Does semolina have any major side effects?
Semolina is generally safe for most people but should be avoided by those with gluten allergies or wheat sensitivities. Overconsumption may contribute to weight gain if not balanced with other foods.
Q: Can semolina be included in a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Yes, semolina is entirely plant-based. However, some recipes include dairy or eggs, so vegans should check or modify recipes accordingly.
Tips for Including Semolina in Your Diet
- Balance with Other Nutrients: Pair semolina with vegetables, legumes, or lean proteins for a nutrient-dense meal.
- Watch Portions: To support weight management and blood sugar control, serve modest quantities and avoid heavy additions of ghee, sugar, or oil.
- Try International Recipes: Experiment with global cuisines—Italian pasta, Indian upma, Turkish helva, or Mediterranean desserts.
Conclusion
Semolina is a nutrient-dense, versatile flour that can be a healthy addition to most diets. By understanding its nutritional benefits, potential drawbacks, and a range of culinary uses, you can enjoy semolina’s unique flavor and texture while supporting your health and well-being. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have known wheat or gluten sensitivities before introducing semolina into your regular meals.
References
- https://www.ndtv.com/health/10-reasons-why-you-must-add-semolina-to-your-diet-7488345
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/semolina
- https://www.tataaig.com/knowledge-center/health-insurance/health-benefits-of-suji
- https://www.lybrate.com/topic/semolina-flour-suji-benefits-and-side-effects
- https://www.medicinenet.com/how_is_semolina_different_from_flour/article.htm
- https://consensus.app/home/blog/health-benefits-of-semolina-flour/
- https://www.grapetree.co.uk/blog/what-is-semolina-is-it-healthy-and-how-to-use-it
- https://www.fmnfoods.com/2021/02/24/8-great-benefits-of-semolina-flour/
Read full bio of Sneha Tete