Muscular System For Kids: 13 Fun Facts To Know
Intriguing facts that teach kids about the muscular system and its functions.

Image: ShutterStock
In This Article
Do you know what helps your fingers make a fist or moves your eyes to read a text? If not, it’s time to get into some muscle facts for kids and find the answers!
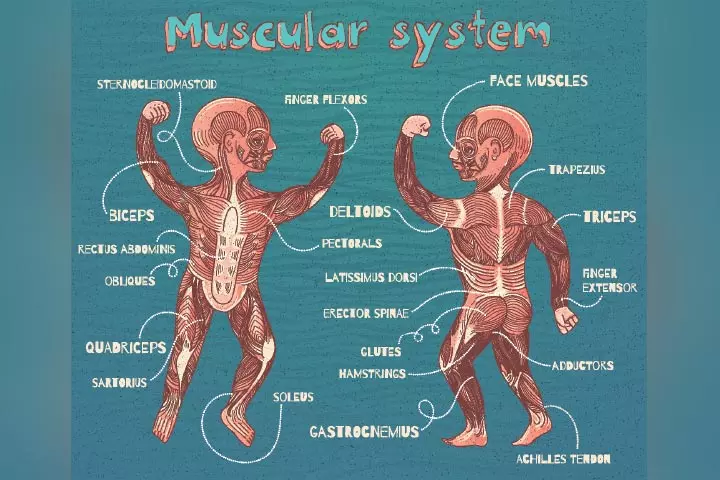
Muscles are a group of tissues that relax and contract so that your skeletal system can stretch. The stretchability of muscles allows the body to do voluntary and involuntary movements, such as breathing and walking (1). More than 600 muscles in the body form the muscular system. The muscular system is an organ system that, together with the skeletal system, forms the musculoskeletal system, helping humans move.
Read this post to know more interesting muscle facts and understand the muscular system better.
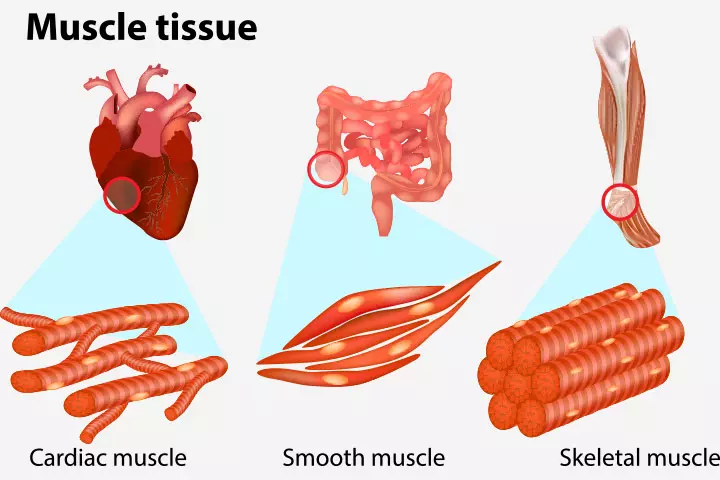
Types of muscles
Humans start building muscles right after birth. Muscles continue to develop until the age of 30 years, after which they deteriorate with age (2).
The human body comprises three kinds of muscles:
- Skeletal muscle: Also known as voluntary muscle, skeletal muscle is attached to bones that help you move your body. Long and cylindrical, skeletal muscle enables you to pull bones to move different parts of the body.
- Smooth muscle: These muscles are found in the bladder and the blood vessels.
- Cardiac muscle: As the name suggests, this type of muscle helps the heart pump blood.
Actions of muscles are classified as voluntary or involuntary.
- Voluntary muscles are the ones that are under your control. Skeletal muscles are the only muscles that move on voluntary action. You can consciously control and move the voluntary muscles, such as the ones in your arms and legs, at your command and direction.
- Cardiac muscle is an involuntary muscle. The heart is an involuntary muscle that beats whether you are awake or asleep. Cardiac muscle contracts to pump blood through the network of veins.
- Smooth muscles are involuntary, much like a cardiac muscle. They are present in the gastrointestinal system, blood vessels, and body hair. With the gastrointestinal system’s help, the stomach and intestine muscles move food through the digestion processes. The smooth muscle of the blood vessels controls the blood pressure, while the muscle in hair follicles controls the erection of body hair.
Muscle Structure
A muscle comprises hundreds and thousands of cells that contract to produce a force. On contraction, the muscle squeezes to appear shorter and expands when blood pumps into the nerves. The nerve cells transfer messages to the muscle cells to make a movement or respond to a sensation.
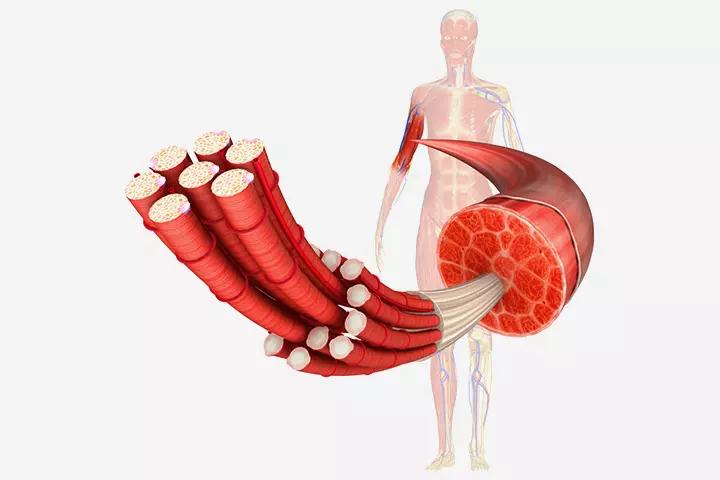
Actin and Myosin are two proteins found in muscle cells. The muscle responds to contraction and expansion due to the presence of the two proteins. Consumption of protein is essential for strong muscles, and our body needs twice the protein percentage than our weight (3). If a person weighs 40 kg, then his body requires 80g protein for maintaining healthy muscle.
What Can Cause The Muscles To Hurt?
Myalgia is a medical term used for describing muscle pain. It can occur due to stress, tension, heavy work, and minor injuries. The pain becomes unbearable when it spreads to other body muscles. Tenderness, redness, swelling, and fever are common symptoms of Myalgia (4).
Usually, mild pain subsides in a few hours. If the entire body suffers pain, then it is called systemic muscle pain. Such pain can be caused due to medicinal side effects, illness, or infection.
Common causes of muscle pain include:
- Sprains
- Muscle cramp
- Myofascial pain syndrome
- Repetitive strain injuries
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Coronavirus infection (COVID-19)
- Rheumatoid arthritis (inflammatory joint disease)
- Influenza (flu) and other viral illness (influenza-like illness)
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) (underactive thyroid)
- Polymyositis (an inflammatory disease that causes muscle weakness)
- Medications, especially the cholesterol medications known as statins
Muscle Contraction
When a nerve communicates the muscle to contract, the muscle opens its cell membrane. The cell membrane includes protein, which is a calcium channel. During contraction, the protein and calcium together stick to form advanced actin and myosin proteins. This allows the muscle to contract and expand to move.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is important for contraction. ATP is formed by the glucose present in muscle cells (5). ATP consumes energy to release contracted muscle and utilizes a major percentage of energy for building muscles.
Exercising The Muscles
Regular exercise and a balanced diet lead to healthier and bigger muscles. Without regular exercise, the body could fall prey to atrophy (6), a condition that makes muscles weak and small. A walk for at least 30 minutes in a day and a healthy and balanced diet, including a good proportion of protein, carbohydrate, minerals, vitamins, and calcium, are essential to keep your muscles strong and healthy.
Some of the easy exercise for kids to try to strengthen their muscles are:
- Squats
- Burpees
- Planks
- Pushups
- Leg raises
- Handstands
Muscle Diseases
Muscle diseases are classified into three categories.
- Neuromuscular diseases: This type of muscle disease weakens the nervous system that transfers messages for muscle movement. Conditions such as cerebral palsy, strokes, and Parkinson’s disease fall under this category.
- Motor endplate diseases: This affects nerve and muscle communication, which is necessary for muscle movement. Myasthenia Gravis and Tetanus are two Motor endplate diseases.
- Myopathies: Causes problems in the muscle structure. Myopathies lead to Muscle Dystrophy, Cancers (Myopathies, Cardiomyopathy, and Ewing’s Sarcoma).
Read on for some more muscle facts that can intrigue children.
Muscle Facts For Kids
- Muscle is a soft tissue found in the human and animal body. The primary function of a muscle is to produce motion and force.
- Skeleton muscles are known as Musculoskeletal systems.
- The muscular system is responsible for enabling physical movement, posture, and movement of internal organs.
- The term muscle is derived from the Latin word “musculus,” which means little mouse.
- Tendons attach soft muscles to hard bones.
- The human body has 600 muscles (1).
- Skeletal muscle is divided into two categories: Slow twitch and fast twitch (7).
- Slow twitch muscle (Type I) has proteins that make it appear red. Slow twitch muscle carries a high percentage of oxygen and utilizes fats, proteins, or carbohydrates as energy.
- Fast twitch muscle (Type II) appears whiter in color and includes less myoglobin (an oxygen-carrying protein). These muscle fibers contract fast, but they soon get fatigued.
- Muscle tissues are denser compared to fat cells.
- We are able to smile when 17 muscles act together, while it takes 43 muscles to make a sad or angry face.
- The eye’s external muscles have 100 times more strength than is needed for eye movements (8).
- There are only eight muscles in the tongue, but they allow in the tongue’s complex movement and help us speak (10).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can little kids get muscles?
Muscle building does not happen before puberty. After puberty, the male hormone testosterone supports muscle development, especially during weight training. As the hormone occurs at higher levels in males, boys usually develop bulkier muscles than girls (1).
2. Does building muscle as a kid stunt growth?
Strength training is usually performed to improve muscle strength and bulk and is considered safe in children if done under appropriate supervision. So, compared to adults, it does not increase the bulk of muscles in children but improves muscle strength and sports performance. Therefore, it will not lead to stunted growth (10).
Muscular system facts for kids can help them understand the system and its functioning. Muscles comprise tissues and cells that relax and contract to enable the movement of body parts. Over 600 muscles in the body form the muscular system. The muscles include skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and voluntary muscles. This post also discusses muscle structure, muscle diseases, and several exercises for muscles to give your child a complete idea about the muscle system.
Key Pointers
- There are more than 600 muscles in the body, forming the muscular system.
- The muscular system enables physical movement, posture, and movement of internal organs.
- Muscles are composed of the proteins actin and myosin, and regular exercise and a balanced diet lead to their healthy growth.
- Muscle disorders are classified into neuromuscular diseases, motor endplate diseases, and myopathies.
References
2. Preserve Your Muscle Mass; Harvard Health Publishing (2016)
3. Daniel Pandick; How Much Protein Do You Need Every Day?; (2019) Harvard Health Blog
4. Muscle Disorders; MedlinePlus.gov
5. Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation; The University of Hawaii
6. Muscle Atrophy; MedlinePlus.gov
7. Quinn, E.; Fast and Slow Twitch Muscle Fibers: Does muscle type determine sports ability?
8. Burton J. Kushner; Eye Muscle Problems in Children and Adults: A Guide to Understanding; University of Wisconsin
9. Frank Gaillard et a; Muscles Of The Tongue; Radiopaedia
10. Strength training by children and adolescents; American Academy of Pediatrics

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Akanksha Allahbadia Gupta