Lotus Root: Nutrition, Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
Discover the nutritional value, medicinal benefits, and culinary versatility of lotus root for holistic health and wellness.
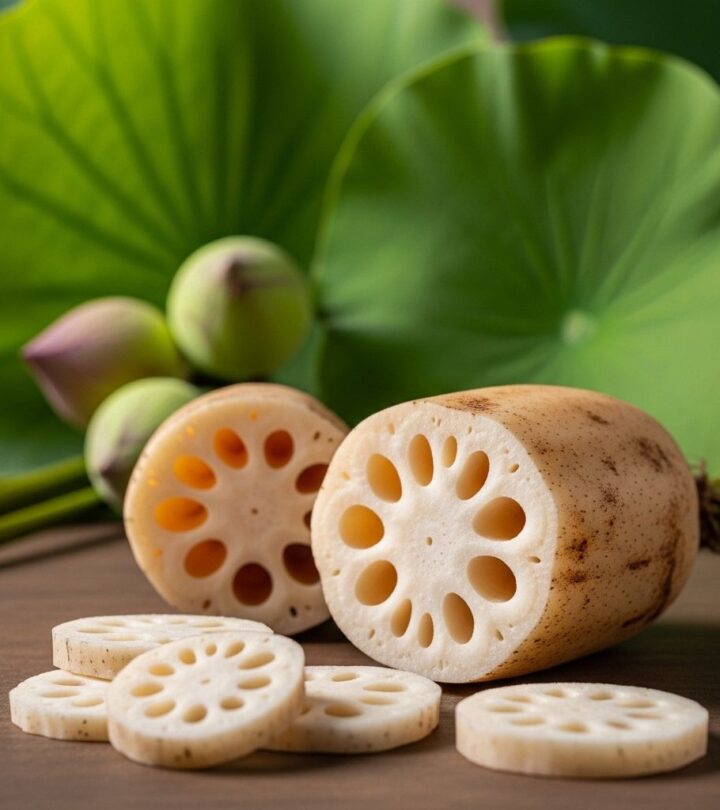

Image: ShutterStock
Lotus Root: Nutrition, Health Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
Lotus root, also known as Nelumbo nucifera, is a versatile root vegetable widely used in Asian cuisine and traditional medicine. Not only cherished for its crunchy texture and mild flavor, lotus root is packed with essential nutrients and offers a multitude of health benefits. From aiding digestion to supporting heart health, lotus root stands out as an exceptional addition to a balanced diet. This article explores the nutritional value, diverse health benefits, culinary uses, and potential side effects of lotus root.
What is Lotus Root?
Lotus root is the elongated, tuberous root of the lotus plant. Typically found submerged in ponds and lakes, the rhizome resembles a long squash that can grow up to 4 feet in length. Lotus flowers are symbolic in many Asian cultures, representing purity, innocence, and beauty. The root is harvested for consumption throughout the year and is enjoyed in raw, stir-fried, steamed, braised, and sautéed dishes.
- Appearance: Cylindrical and segmented, creamy-white inside, with a mild sweet flavor and crunchy texture.
- Culinary versatility: Used in soups, salads, pickles, chips, and teas.
Nutritional Value of Lotus Root
Lotus root is low in calories and cholesterol, yet densely packed with essential nutrients. Its unique mix of vitamins, minerals, protein, and dietary fiber contribute to multiple physiological functions.
| Nutrient (Per 100g) | Amount | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~74 kcal | Low-calorie vegetable |
| Protein | ~2.6 g | Supports tissue repair |
| Dietary Fiber | ~4.9 g | Promotes digestion |
| Vitamin C | ~44 mg | Immune support, antioxidant |
| Vitamin B6, Thiamin, Pantothenic Acid | Present in modest amounts | Energy metabolism, mood regulation |
| Potassium | ~556 mg | Regulates heart rhythm, blood pressure |
| Phosphorus, Copper, Iron, Manganese, Zinc | Present in beneficial amounts | Blood formation, metabolism, cellular health |
The root’s rich mix of vitamins B2, B6, and C supports energy metabolism, immune function, collagen synthesis, and more. Lotus root’s dense fiber content aids digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar.
Major Health Benefits of Lotus Root
Lotus root is revered for its multifaceted health advantages, from improving cardiovascular health to strengthening the immune system. Here are its top scientifically supported benefits:
1. Promotes Healthy Skin
- High in Vitamin C: Essential for collagen synthesis and protecting skin against oxidative stress and aging.
- Reduces hyperpigmentation and skin discoloration.
- Possesses anti-aging and anti-wrinkle properties, inhibiting skin damage.
2. Boosts Brain and Mental Health
- Copper and B complex vitamins stimulate neural pathways and assist in the production of neurotransmitters.
- May help regulate mood, mental clarity, and reduce symptoms of depression and stress.
- Polyphenolic compounds stimulate neurotrophic factors, supporting cognitive health.
3. Enhances Circulation and Energy Levels
- Rich in iron and copper: Promotes red blood cell formation and improves oxygenation throughout the body.
- Regulates blood flow, increasing overall energy and vitality.
- Bioactive polysaccharides support metabolism and prevent fatigue.
4. Supports Digestive Health and Weight Management
- High dietary fiber boosts stool bulk, alleviating constipation and improving regularity.
- Promotes satiety, helping in weight management and curbing hunger.
- Aids nutrient absorption through stimulated gastric juice release.
- Fermented lotus root may offer gastroprotective benefits.
5. Improves Cardiovascular Health
- Potassium acts as a vasodilator, relaxing blood vessel walls, reducing rigidity, and lowering blood pressure.
- Dietary fiber helps remove cholesterol, supporting arterial health.
- Pyridoxine regulates homocysteine levels, further aiding heart health.
6. Boosts Immunity
- Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, neutralizing harmful free radicals.
- Supports collagen production for strong skin, vessels, and organs.
- May prevent some forms of cancer and chronic diseases.
7. Regulates Blood Sugar and Prevents Diabetes
- Complex carbohydrates provide slow-releasing energy and help control blood sugar levels.
- Animal studies suggest lotus compounds may lower blood sugar, beneficial for diabetic management.
8. Liver and Stomach Protection
- Plant compounds have been shown to protect the liver and stomach from inflammation and damage.
- Antioxidant effects further strengthen cellular resilience to toxins.
9. Treats Respiratory Issues
- Helps clear accumulated mucus and relieve coughs.
- Lotus root juice may be used to treat conditions like tuberculosis and asthma.
10. Benefits Eye and Hair Health
- Rich in Vitamin A: Prevents macular degeneration, ocular conditions, and skin inflammation.
- Supports strong hair and healthy eyes due to antioxidant properties.
11. Treats Fungal Infections and Bleeding Disorders
- Helps combat conditions like ringworm and leprosy.
- Lotus leaves can alleviate excessive sweating, fever, nosebleeds, and blood in urine.
Culinary Uses of Lotus Root
Lotus root is prized for its delicate crunch and mild sweetness, offering an exciting texture in various dishes. It is prepared and consumed in diverse ways across Asia and other parts of the world.
- Raw: Thinly sliced for salads.
- Stir-fried or Sautéed: Common in Chinese and Japanese cuisine.
- Steamed or Braised: Used in soups and stews for a tender consistency.
- Pickled: Marinated and preserved for snacks and side dishes.
- Chips: Sliced thin and deep-fried for a crunchy snack.
- Tea and Powder: Lotus root tea and powder are available for drinks and as supplements.
| Preparation | Description |
|---|---|
| Soup | Sliced lotus root cooked in broths with meat or vegetables |
| Salad | Raw or blanched slices tossed with spices, vinegar, and sesame oil |
| Chips | Deep-fried slices served as snacks |
| Tea | Infused slices or powdered root in hot water, often for medicinal use |
The root’s ability to complement both savory and sweet profiles makes it a favorite journey from kitchens to herbal remedies.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
While lotus root is generally safe and nutritious, individuals should be aware of some potential cautions:
- Allergic Reactions: Rare but possible; observe for skin rashes or digestive discomfort after consumption.
- Contamination: As an aquatic vegetable, lotus root is susceptible to microbial contamination when grown in polluted waters. Ensure purchase from reputable sources.
- Overconsumption: Excessive intake may lead to gastrointestinal upset due to high fiber.
- Raw Consumption: Raw lotus root may harbor parasites or bacteria if not washed and handled properly.
Lotus Root in Traditional Medicine
Lotus root has been an essential component in Eastern traditional medicine for centuries, recognized for its restorative properties:
- Used to treat coughs, fever, and digestive disorders.
- Employed for its calming effects and as a tonic for vitality and longevity.
- Known to relieve respiratory and bleeding disorders, as referenced in Ayurveda and Chinese medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What does lotus root taste like?
A: Lotus root has a slightly sweet, crisp flavor, similar to a water chestnut, with a distinct crunchy texture.
Q: Can lotus root be eaten raw?
A: Yes, lotus root can be eaten raw when sliced thin, although it should be thoroughly washed. It’s also often cooked or blanched for salads.
Q: How do you store lotus root?
A: Store in a cool, dry place or refrigerate in a sealed container. Keep unpeeled to avoid oxidation and dryness.
Q: Is lotus root safe during pregnancy?
A: Generally yes, lotus root offers valuable nutrients beneficial during pregnancy. However, consult a doctor for individual recommendations.
Q: What are the most popular lotus root recipes?
A: Lotus root soup, stir-fried lotus root with vegetables, braised lotus root, pickled lotus root, and lotus chips are popular recipe choices.
Conclusion
Lotus root stands as a potent superfood, combining remarkable nutritional density, medicinal efficacy, and culinary versatility. By adding lotus root to your daily diet, you can benefit from enhanced digestion, immunity, cardiovascular health, and more. As with any food, moderation and proper preparation ensure you reap its advantages without risk.
References
- https://draxe.com/nutrition/lotus-root/
- https://www.lybrate.com/topic/benefits-of-lotus-root-and-its-side-effects
- https://sakura.co/blog/lotus-root-everything-you-need-to-know
- https://www.healthline.com/health/8-uses-for-lotus
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2994372/
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/lotus-roots-its-culinary-uses-and-health-benefits/photostory/85211638.cms
Read full bio of Medha Deb