Juniper Berries: Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and More
Explore the health benefits, traditional uses, nutritional values, and safety tips related to juniper berries, with evidence-based insights and FAQs.
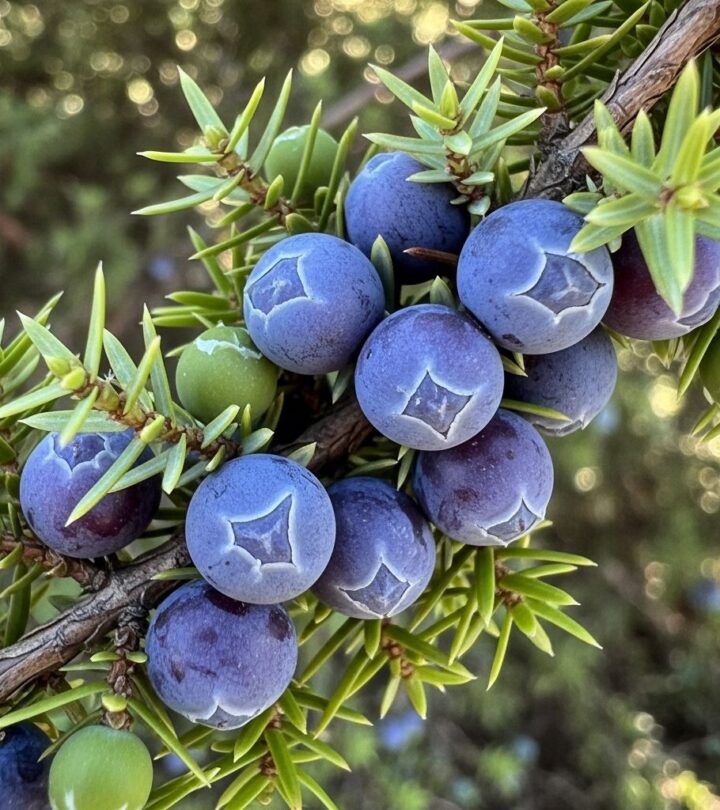

Image: ShutterStock
Juniper berries, famed for their sharp, pine-like flavor and distinctive aroma, are not true berries but the seed cones of various juniper species, primarily Juniperus communis. For centuries, these bluish fruits have played significant roles not just in culinary traditions but also in herbal, medicinal, and ceremonial practices across Europe, Asia, and North America. This guide explores the multifaceted benefits, uses, nutritional profile, and important safety considerations of juniper berries based on the latest research and traditional wisdom.
What Are Juniper Berries?
Juniper berries grow on evergreen shrubs belonging to the cypress family. Although commonly called berries, they are actually seed cones with fleshy exteriors, recognizable by their rich blue or purple hues.
- Origin: Europe, North America, Asia
- Common Species: Juniperus communis (the most widely used), among others.
- Culinary Use: Spice for meats, game, sauerkraut, beverages (notably gin due to their essential oil).
- Traditional Uses: Herbal medicine, antiseptic, preservative, incense.
Ancient civilizations revered juniper berries for their purifying properties and medicinal value, and these traditions continue in various modern herbal practices.
Nutrition Profile of Juniper Berries
Though consumed in small quantities, juniper berries are rich in valuable vitamins and phytochemicals:
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant supporting immune function and skin health.
- Flavonoids: Such as rutin, luteolin, apigenin; contribute to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Volatile Oils: Including alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, limonene, myrcene, sabinene—give berries their aroma and medicinal value.
- Coumarins: Bioactive compounds present in various medicinal plants.
These compounds work synergistically to support various bodily systems, especially when used as part of an overall healthy diet and lifestyle.
Health Benefits of Juniper Berries
1. Potent Source of Antioxidants
Juniper berries are loaded with antioxidant compounds, such as flavonoids and vitamin C, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body.
- Antioxidants protect against cell damage, supporting overall health and possibly lowering disease risk.
- Specific compounds like rutin and sugiol contribute to cellular protection and have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved immune response.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Essential oils and flavonoids in juniper berries provide anti-inflammatory effects. Research has shown that monoterpenes like limonene and alpha-pinene help modulate the body’s inflammatory response.
- These properties can help alleviate muscle and joint pain, tendonitis, and general inflammation.
- Traditionally used to soothe sore throats, bronchitis, and digestive tract inflammation.
3. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
The essential oils found in juniper berries exhibit notable antimicrobial effects.
- Effective against fungi like Candida (a common cause of skin infections).
- Inhibitory effects on bacterial strains such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Campylobacter jejuni, which are associated with skin, lung, and urinary infections.
4. May Improve Heart Health
Some studies suggest that juniper berry extracts can improve lipid profiles and may help protect cardiovascular health.
- Research in animals indicates juniper berries can lower total cholesterol and triglycerides and promote healthy HDL (good cholesterol) levels while reducing LDL (bad cholesterol).
- Their diuretic effects may help maintain healthy blood pressure.
However, more human studies are needed to confirm cardiovascular benefits.
5. Potential Antidiabetic Properties
Juniper berries have been used in folk medicine to manage blood sugar levels, and emerging research supports their potential.
- Flavonoids like rutin and amentoflavone in the berry may stimulate insulin production and improve glucose uptake.
- Animal studies have demonstrated reduced blood sugar and improved lipid profiles with juniper supplementation.
- Further research in humans is necessary.
6. Diuretic and Detoxifying Effects
Juniper berries possess mild diuretic properties, encouraging the elimination of excess fluid and toxins from the body.
- May relieve fluid retention and support kidney function.
- Historically, used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) and support detoxification.
7. Digestive Aid
Traditionally, juniper berries have been used to ease digestive complaints.
- May help relieve bloating, gas, and indigestion.
- Used as a carminative agent to promote healthy digestion and appetite.
8. Analgesic and Sedative Properties
Compounds such as pinene and linalool have mild analgesic (pain-relieving) and sedative effects.
- May help with minor aches, headaches, and promote relaxation.
- The aroma of juniper oil is used in aromatherapy to reduce stress and support restful sleep.
9. Respiratory Benefits
Inhalation of juniper berry essential oil vapor is believed to offer relief from respiratory symptoms.
- May help with bronchitis, asthma, and coughs due to anti-inflammatory effects in the airways.
10. Skin Health Support
Juniper berry’s antibacterial and anti-inflammatory actions make it useful for skin care.
- Applied as diluted oil or added to skincare products for acne, eczema, psoriasis, dandruff, and to cleanse the skin.
- Astringent properties help tone and clarify the skin.
Traditional and Modern Uses of Juniper Berries
- Culinary Uses: Spice in dishes including wild game, stews, and fermented foods. Principal botanical in gin.
- Herbal Remedies: Decoctions, teas, tinctures, extracts, and essential oil for various ailments.
- Aromatherapy: Essential oil used for relaxation, improved sleep, and respiratory benefits.
- Topical Applications: Diluted oil added to lotions, creams, or applied with a carrier oil for inflammation and skin health.
How to Use Juniper Berries
- Whole Berries: Crushed before adding to recipes for flavor release.
- Juniper Tea: Steep 1-2 teaspoons of dried berries in hot water for 10-15 minutes.
- Extracts and Tinctures: Used as herbal supplements; follow dosage instructions carefully.
- Essential Oil: For aromatherapy or diluted topical use. Never ingest essential oil directly.
Possible Side Effects and Safety Precautions
- Generally safe when used as a culinary spice or in moderate herbal practice.
- Potential Risks:
- May cause kidney irritation with high or prolonged use.
- Possible stomach upset, diarrhea, or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Should not be used by pregnant or breastfeeding women due to risk of uterine contractions and insufficient safety data.
- Avoid if you have chronic kidney disease or are taking diuretics, lithium, or blood sugar medications due to potential interactions.
Nutritional Comparison Table: Juniper Berries vs. Other Berries
| Berries | Vitamin C | Key Compounds | Special Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Juniper Berries | Present | Essential oils, flavonoids, coumarins | Antimicrobial, diuretic, digestive aid |
| Blueberries | High | Anthocyanins, vitamin E | Antioxidant, eye health |
| Cranberries | Moderate | Proanthocyanidins | Urinary tract support |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are juniper berries safe to eat?
A: Juniper berries from Juniperus communis are generally safe when used as a spice or in small amounts as a herbal remedy. Do not consume berries from ornamental juniper species, as some can be toxic. Always consult an expert before wild foraging.
Q: What do juniper berries taste like?
A: Juniper berries have a sharp, aromatic, and pine-like flavor with hints of citrus, making them unique among culinary spices.
Q: Can juniper berries help with urinary tract infections?
A: Traditional medicine supports their use for UTIs due to diuretic and antimicrobial properties, but clinical evidence is limited. Consult a healthcare provider for persistent infections.
Q: Is it safe to use juniper berry essential oil directly on the skin?
A: No, juniper berry essential oil must be diluted in a carrier oil before topical use to avoid skin irritation.
Q: Who should avoid juniper berries?
A: Pregnant and breastfeeding women, children, people with kidney disease, or those taking certain medications (like diuretics, lithium, or diabetes drugs) should avoid juniper berry supplements and consult a healthcare professional before use.
Conclusion
Juniper berries are a versatile, traditional botanical offering a wealth of potential health benefits, from antioxidant protection to digestive support and antimicrobial action. Used wisely—as a spice, herbal remedy, or aromatherapy aid—juniper can complement a healthy lifestyle. However, some people should exercise caution, and best practices include seeking professional advice before adopting juniper as a supplement or topical agent. Enjoy the distinctive flavor of juniper berries while respecting their potency and tradition.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/juniper-berries
- https://www.tuasaude.com/en/juniper-berry/
- https://draxe.com/nutrition/juniper-berries/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6726717/
- https://www.todaysdietitian.com/herbs-spices-juniper-berries/
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/what-to-know-juniper-berries
- https://www.newdirectionsaromatics.com/blog/juniper-berry-essential-oil-uses-benefits-and-recipes/
- https://www.medicinenet.com/juniper/article.htm
- https://www.peacehealth.org/medical-topics/id/hn-2117006
Read full bio of Medha Deb