IUD Birth Control: Types, Advantages And Disadvantages
Intrauterine device (IUDs) types significantly determine the benefits you get in the long run.
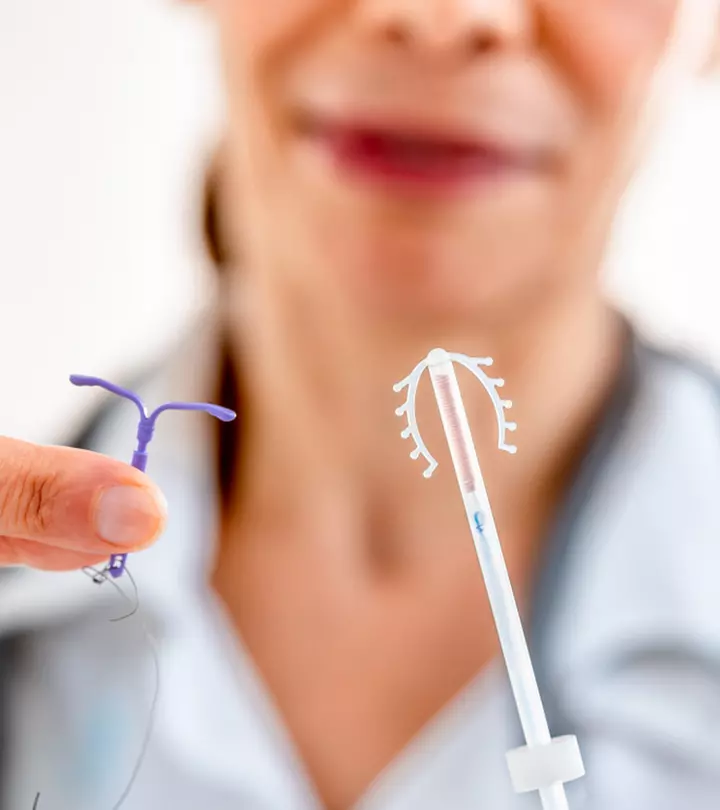

Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) or intrauterine contraception devices are among the most popular birth control measures. IUDs are available in two variants: hormonal and non-hormonal. These tiny devices are placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancies for three to ten years. They function by preventing the sperm from fertilizing the egg and making changes in the uterus.

Read this post to learn about the types, uses, advantages, and associated risks of using an IUD.
What Are The Types Of IUDs?
IUDs are available in hormonal and non-hormonal variants.
1. Non-hormonal IUDs
They are medical contraception devices, usually with copper as the active ingredient.
- Copper frame IUD: These are T-shaped soft polymer devices wrapped with a thin layer of copper wires. These can be safely used up to ten years at a stretch.
- Frameless IUD: A modern variant of copper IUD comes with a frameless design that lacks a large T-shaped frame. Here, a hollow copper tube is wrapped over a polypropylene thread. This design allows minimal discomfort and molds easily into the shape of the uterus (1).
2. Hormonal IUDs
These are T-shaped, polymer-based devices containing the hormone progestin. These devices are placed in the uterus, where they release the hormone progestin. The hormonal IUDs help control heavy periods, and they are often used during estrogen replacement therapy (2) (3).
How Do IUDs Work?
The non-hormonal IUDs use copper, which is a spermicidal agent that affects sperm quality, making it nearly impossible for it to fertilize the egg. The hormonal IUDs work by primarily preventing ovulation and altering the cervix lining, making fertilization and implantation of an egg almost impossible.
Below are other attributes of the functioning of IUDs.
- Non-hormonal copper IUDs do not directly prevent fertilization. They release copper ions in the uterus. It leads to a “foreign body effect,” an inflammatory reaction in the intrauterine cavity, making the endometrium (lining of the uterus) unfavorable for implantation of the zygote. This inflammatory reaction also causes the release of prostaglandins, and white blood cells (WBC) are released within the uterine and tubal fluids. Thus, a combination of copper ions, hormones, and WBC has a toxic effect on spermatozoa and oocytes in the uterus.
- Hormonal IUDs work by releasing a type of hormone, progestin, in the uterus. Progestin is a synthetic form of progesterone hormone that makes the uterus unfriendly to sperm. In addition, the progestin hormone causes thinning of the uterus lining and partly suppresses ovulation. Progestin-containing IUDs also help control heavy menstrual periods in some women. In addition, estrogen replacement therapy patients, having an excessive build-up of the uterus lining, use them to clear out the endometrium.
How Effective Is An IUD?
IUDs are reliable contraception methods and provide more than 99% efficiency (4). However, no method of contraception is 100 % effective, and there is always a chance of getting pregnant.
How Long Does An IUD Work?
According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the copper IUD will safely work over three to ten years. The hormonal IUDs are approved to work from three to five years (5).
How Is An IUD Inserted?
The IUDs are prescription medical devices and should only be inserted by a qualified medical practitioner. IUDs are preferably inserted immediately after menses or after the heavy flow of menses settles by day three or four. During this time, the cervix is open and hence more receptive to introducing IUDs without much discomfort to the woman. During the intrauterine device insertion, a short procedure will be followed (6).
- The vagina and cervix will be examined using a vaginal speculum. Then, the body parts will be cleaned using a cleaning solution.
- A special instrument will be used to align the cervical canal and the uterine cavity.
- The depth of the uterine cavity will be measured.
- The horizontal arms of the T-shaped IUD will be folded, and using an applicator tube, the device is delivered into the uterus.
- Lastly, the extra-long thread at the bottom of the IUDs is shortened.
- Sometimes a small yet significant length of the thread attached to the IUD is left behind in the vagina for the woman to periodically check the presence of IUD in utero when in doubt. The presence of thread on palpation or touch indicates the presence of the IUD inside the uterus. If the thread is not felt, it could either be because of the coiling of the thread or due to a misplaced or fallen IUD.
- In conditions when the thread cannot be palpated or felt. The woman should immediately consult the doctor and use alternative methods of contraception (condoms or pills) till it is either confirmed clinically by the doctor (on visual examination of the thread on the examination table) or radiologically using X-ray or ultrasonography.
Frameless IUD is inserted using a specialized instrument directly into the myometrium of the uterine fundus. The optimal insertion period is right after the menstrual cycle, although it can be done anytime. The procedure of insertion might be painful and may cause cramping in some women.
A qualified medical practitioner should also carry out the removal of IUD. The IUDs come with two monofilament threads to aid in the removal. A force is used to gently pull out the IUD, which will fold upward and come out.
What Are The Advantages Of An IUD?
IUDs let the woman have intercourse without having to worry about male contraception. IUDs generally offer the following benefits.
- IUDs reduce the risk of unwanted pregnancy: You do not have to worry about contraception, and it may make intercourse more convenient.
- Work from three to ten years: You do not have to remember using or having an IUD since it is always there.
- Reversible nature: An IUD can be removed anytime to regain your fertility.
Each type of IUD comes with its specific advantages and should be selected by consulting a qualified doctor (2) (7).
Advantages of copper IUDs are:
- Copper IUDs are the choice of action to avoid hormonal alternatives.
- It can be safely used by women who have never given birth.
- It lets you avoid any potential side effects of hormones from hormone IUDs.
- You can use them while on medications.
Advantages of frameless IUDs are:
- The design does not have a bulky structure. As a result, they are comfortable to use compared to the conventional T-shaped design.
- They significantly reduce pain, abnormal bleeding, and embedment.
- They have a low risk of expulsion, reducing the chance of pregnancy.
- The frameless design adapts to the shape of the uterus.
Advantages of hormonal IUDs are:
- They reduce menstrual bleeding and pain.
- They reduce the risk of endometrial cancer.
- They reduce the risk of pelvic infection.
- They offer less risk than direct estrogen-based birth control measures.
- The use of hormonal IUDs over a long time may lead to the cessation of periods in some women.
What Are The Disadvantages Of An IUD?
IUDs do come with their share of drawbacks that you may discuss with your doctor (8).
- Framed IUDs may not comfortably fit all types of uterus. Poor fit may cause discomfort and pain during menstruation. Some IUDs may slip out due to a poor fit. If it happens during or after intercourse, there could be a risk of pregnancy.
- Copper IUDs are associated with the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). They are not recommended for women with existing pelvic infections. They are also not recommended for women with copper allergy, Wilson’s disease, and certain cancers.
- IUDs are not 100% effective, and there is still a chance of pregnancy. In such cases, the presence of the IUD may affect the health of the growing fetus and the mother. It may also lead to infertility in some cases.
- Hormonal IUDs may cause acne, headaches, mood swings, breast tenderness, irregular bleeding, cramping, and pelvic pain.
- You may not be able to take certain medications if you use a hormonal IUD.
- Some women may take time to regain fertility on the removal of an IUD.
- IUDs do not protect you from sexually transmitted infections, and you still have to use contraceptives such as condoms.
- Hormonal IUDs are not recommended for women with or with a history of breast, cervical, or uterine cancer. It may also not be suitable for a few women with liver disease and uterine abnormalities.
- Hormonal IUDs are usually advised after at least six to eight months post-delivery to avoid uterine damage.
- Hormonal IUDs may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Some women may experience longer and heavier periods while using an IUD.
How Much Does An IUD Cost?
The cost of IUDs depends on the choice of device, government norms, and the medical facility provider. The cost of an IUD can be up to $1300 in the US (7) (9). Most insurance providers cover the cost of IUDs in the US, and the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has further ensured that women do not have to bear a high cost of IUDs. You may contact your local healthcare provider’s clinic for specific details regarding the cost of IUD in your area.
When To Call The Doctor?
While using an IUD, it is advisable to seek a healthcare provider if you notice the following symptoms (10).
- Severe bleeding or abdominal pain
- Menstrual cycle stops suddenly
- Device falls out
- You do not feel the string of the IUD
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can IUDs be used as emergency contraception?
IUDs may be used as emergency contraception. Hormonal and copper IUDs should be placed within three and five days of unprotected sex, respectively. However, it may not always prevent pregnancy, so you must not entirely rely on it for the prevention of pregnancy.
2. Can my partner feel it?
Your partner usually cannot feel anything. In rare cases, the string attached to the IUD could be felt, although it does not interfere with intercourse.
IUDs are long-acting, reversible contraceptives and remain active for three to ten years. In addition, hormonal IUDs may help reduce excessive bleeding and pain during menstruation. The copper IUDs are the choice of contraception if someone wants to avoid hormonal alternatives. You may pick the right IUD after a discussion with your healthcare provider.
Key Pointers
- Intrauterine contraception devices (IUDs) can be hormonal or non-hormonal.
- Hormonal IUDs prevent ovulation and alter the cervical lining to prevent pregnancy.
- Non-hormonal IUDs are made from copper, a spermicidal agent that alters sperm quality.
References
- Intra-uterine Devices.
https://www.aiims.edu/aiims/events/Gynaewebsite/ec_site/manual/7_intra-uterine.htm - Dirk Wildemeersch et al.; (2015); Intrauterine systems: a frameless future?
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1517/17425247.2016.1162153?journalCode=iedd20 - Jennifer K. Hsia et al.; (2016); Intrauterine Contraception.
https://escholarship.org/content/qt9w32p2s2/qt9w32p2s2_noSplash_5eef03704ce3df45308f145fe44740fd.pdf - How effective are IUDs?
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/iud/how-effective-are-iuds - Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Access for Women in the US.
https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/fact-sheet/intrauterine-devices-iuds-access-for-women-in-the-u-s/ - IUD Insertion.
https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/hw7563#hw7563-sec - Contraception – intrauterine devices (IUD).
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/contraception-intrauterine-devices-iud - Intrauterine Device (IUD) for Birth Control.
https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/tw9516 - How can I get an IUD?
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/iud/how-can-i-get-an-iud - Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD,IUCD).
https://www.health.govt.nz/your-health/healthy-living/sexual-health/intrauterine-contraceptive-device-iud-iucd

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.