Dragon Fruit Benefits: Nutrition, Health & How to Enjoy It
Discover the amazing health benefits of dragon fruit and why this exotic superfruit deserves a place in your diet
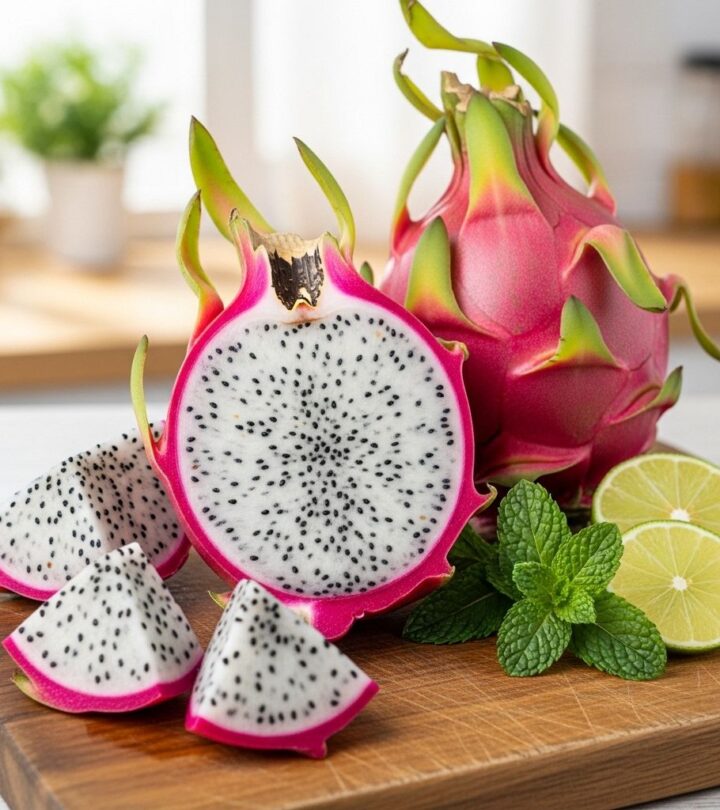

Image: ShutterStock
Dragon fruit, also known as pitaya or strawberry pear, has captivated health enthusiasts worldwide with its striking appearance and impressive nutritional profile. This exotic tropical fruit, with its vibrant pink or yellow skin and white or red flesh speckled with tiny black seeds, offers far more than just aesthetic appeal. From supporting cardiovascular health to boosting immunity, dragon fruit has earned its reputation as a nutritional powerhouse that deserves a prominent place in your diet.
Native to Central America but now cultivated throughout Southeast Asia and other tropical regions, dragon fruit belongs to the cactus family and thrives in warm climates. Its unique combination of essential nutrients, powerful antioxidants, and beneficial plant compounds makes it an exceptional choice for those seeking to enhance their overall health through natural, whole foods.
What Is Dragon Fruit?
Dragon fruit is a tropical fruit that grows on several species of cactus, primarily the Hylocereus genus. The fruit gets its dramatic name from its distinctive appearance, featuring leathery, bright pink or yellow skin with prominent scales that resemble a dragon. When cut open, the fruit reveals soft, sweet flesh that can be white or deep magenta, dotted throughout with small, edible black seeds similar to those found in kiwi fruit.
There are three main varieties of dragon fruit: white-fleshed fruit with pink skin, red-fleshed fruit with pink skin, and white-fleshed fruit with yellow skin. While all varieties offer health benefits, the red-fleshed variety contains higher levels of certain beneficial compounds, particularly betalains, which give the flesh its distinctive crimson color.
The taste of dragon fruit is subtly sweet, often described as a cross between kiwi and pear, with a refreshing, mild flavor that makes it versatile in both sweet and savory dishes. The texture is smooth and slightly crunchy due to the edible seeds, creating a pleasant eating experience.
Nutritional Profile of Dragon Fruit
Understanding the nutritional composition of dragon fruit helps explain why this exotic fruit has gained such popularity among health-conscious consumers. Dragon fruit delivers an impressive array of essential nutrients while remaining remarkably low in calories, making it an excellent choice for those managing their weight or simply seeking nutrient-dense foods.
A serving of 100 grams of dragon fruit contains approximately 57 calories, with minimal fat content at just 0.14 grams and a modest protein content of 0.36 grams. The fruit provides 15 grams of carbohydrates and an impressive 3 grams of dietary fiber, which contributes to digestive health and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
In terms of micronutrients, dragon fruit supplies vitamin C at about 5% of the daily value, supporting immune function and collagen synthesis. The fruit also contains iron at 1% of the daily value and magnesium at 2% of the daily value. While these percentages might seem modest, dragon fruit compensates with its rich antioxidant content and unique bioactive compounds that offer additional health benefits.
Beyond these standard nutrients, dragon fruit contains beneficial plant compounds including polyphenols, carotenoids, and betacyanins. These phytonutrients work synergistically to protect cells from oxidative damage and support various aspects of health, from cardiovascular function to cognitive performance.
Powerful Antioxidant Properties
One of the most compelling reasons to include dragon fruit in your diet is its exceptional antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals—unstable molecules that contribute to chronic diseases, inflammation, and accelerated aging. Dragon fruit contains several distinct types of antioxidants, each offering unique protective benefits.
Betalains, found primarily in red dragon fruit, are deep red pigments that demonstrate remarkable health-promoting properties. Research has shown that betalains can significantly reduce total cholesterol levels, lower LDL (bad) cholesterol, and improve various cardiovascular health markers. These powerful compounds not only provide the fruit’s striking color but also deliver substantial therapeutic benefits.
Hydroxycinnamates represent another important group of antioxidants present in dragon fruit. These compounds have demonstrated promising anticancer activity in laboratory studies, suggesting potential protective effects against cellular mutations and tumor development. While more human research is needed, the preliminary evidence supports dragon fruit’s role in a cancer-preventive diet.
Flavonoids, a large and diverse family of plant compounds, are abundant in dragon fruit. These antioxidants have been extensively studied and linked to improved brain health, reduced risk of heart disease, and protection against cognitive decline. The variety of flavonoids in dragon fruit contributes to its comprehensive health-promoting effects.
Comparative studies examining the antioxidant capacity of tropical fruits have revealed that while dragon fruit may not rank highest in overall antioxidant content, it excels at protecting fatty acids from free radical damage. This specific protective capability is particularly valuable for maintaining cellular membrane integrity and preventing lipid peroxidation.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits
Dragon fruit offers remarkable benefits for cardiovascular health through multiple mechanisms. The fruit’s unique combination of nutrients and bioactive compounds work together to support heart health, improve lipid profiles, and reduce risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease.
Research has demonstrated that consuming dragon fruit, particularly the red variety, can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol levels. Studies have shown reductions in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides, while simultaneously increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels. This favorable shift in lipid profiles is crucial for reducing the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
The mechanisms behind these cardiovascular benefits are multifaceted. Dragon fruit contains high levels of soluble dietary fibers that bind to bile acids in the digestive tract, promoting their excretion and subsequently lowering blood cholesterol levels. The fruit’s polyphenols act as powerful antioxidants that neutralize free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation, thereby protecting blood vessels from damage and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Animal studies have revealed that red dragon fruit can effectively counteract dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and atherosclerosis. The fruit appears to inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, a critical enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis, providing a natural mechanism for cholesterol management similar to statin medications but without pharmaceutical side effects.
Additionally, dragon fruit’s ability to improve insulin sensitivity may indirectly benefit cardiovascular health by mitigating the risk of type 2 diabetes, which is strongly associated with dyslipidemia and increased cardiovascular disease risk. The fruit’s anti-inflammatory properties further contribute to vascular health by reducing chronic inflammation, a key contributor to heart disease.
Supporting Weight Management and Metabolism
For individuals seeking to manage their weight or support healthy metabolism, dragon fruit emerges as an excellent dietary choice. The fruit’s natural composition makes it particularly effective for weight management while providing essential nutrients that support overall metabolic health.
Dragon fruit is naturally low in calories, with just 57 calories per 100 grams, yet high in fiber content. This combination creates a sense of fullness and satiety that can help reduce overall calorie intake throughout the day. The fiber content slows digestion, stabilizes blood sugar levels, and prevents the rapid spikes and crashes that often lead to cravings and overeating.
The fruit’s high water content further contributes to its weight management benefits. Like other hydrating fruits, dragon fruit helps maintain proper hydration while filling the stomach, creating a natural mechanism for appetite control. High-fiber, water-rich foods make ideal snacks because they help keep you satisfied for longer periods between meals without contributing excessive calories.
Research has indicated that dragon fruit may inhibit lipase activity, an enzyme responsible for breaking down dietary fats. By reducing fat absorption in the digestive tract, dragon fruit may help prevent excess calorie storage and support healthy body composition. This effect, combined with the fruit’s ability to improve insulin sensitivity, positions dragon fruit as a promising natural intervention for obesity management.
The fruit’s beneficial effects on lipid metabolism extend beyond simple weight loss. Dragon fruit helps prevent fat accumulation, particularly visceral fat that surrounds internal organs and poses significant health risks. Its ability to support healthier cholesterol levels while promoting fat metabolism makes it valuable for comprehensive metabolic health rather than just weight reduction.
Digestive Health and Gut Support
Dragon fruit provides exceptional support for digestive health through its impressive fiber content and prebiotic properties. A healthy digestive system is fundamental to overall wellness, affecting everything from nutrient absorption to immune function, and dragon fruit offers multiple mechanisms to support optimal gut health.
The substantial fiber content in dragon fruit—approximately 3 grams per 100-gram serving—plays a crucial role in maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Dietary fiber adds bulk to stool and helps it move smoothly through the digestive tract, acting as a gentle, natural laxative. This makes dragon fruit particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing occasional digestive sluggishness or irregularity.
Beyond simple fiber content, dragon fruit contains prebiotics—specialized plant fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotics specifically promote the growth of important probiotic species including lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, which are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Having more prebiotics in your system improves the balance of beneficial bacteria to potentially harmful bacteria in your intestines.
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in numerous aspects of health, from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and even mental health. By nourishing beneficial bacteria, dragon fruit helps create an environment where these helpful microorganisms can thrive and perform their essential functions, including producing vitamins, supporting immune responses, and protecting against pathogenic bacteria.
A healthy gut microbiome supported by dragon fruit consumption can help fight off disease-causing viruses and bacteria more effectively. The beneficial bacteria also assist in breaking down food, extracting nutrients more efficiently, and producing short-chain fatty acids that provide energy for intestinal cells and support overall gut health.
Immune System Enhancement
Dragon fruit serves as a valuable ally in supporting and strengthening the immune system through multiple nutritional pathways. A robust immune system is essential for defending against infections, accelerating healing, and maintaining overall health, and dragon fruit provides several key nutrients that support immune function.
While dragon fruit’s vitamin C content may not be dramatically high compared to citrus fruits, it still contributes meaningfully to immune support. Vitamin C stimulates the production and function of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. It also acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting immune cells from oxidative damage during their battle against pathogens.
The diverse array of antioxidants in dragon fruit—including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and betacyanins—provide additional immune support by reducing oxidative stress throughout the body. Chronic oxidative stress can weaken immune responses and make the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. By neutralizing free radicals, these antioxidants help maintain optimal immune function.
Dragon fruit’s prebiotic fiber contributes indirectly to immune health by supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Approximately 70% of the immune system resides in the gut, and the beneficial bacteria nourished by dragon fruit’s prebiotics play crucial roles in training and regulating immune responses. A healthy gut microbiome helps distinguish between harmful pathogens and beneficial substances, preventing both infections and inappropriate immune reactions.
The fruit also contains selenium, a trace mineral essential for immune function. Selenium supports the production and activity of various immune cells and enhances the body’s ability to respond to infections. Combined with dragon fruit’s other nutrients, selenium contributes to comprehensive immune system support.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Dragon fruit shows promising potential for supporting healthy blood sugar levels, making it particularly valuable for individuals concerned about diabetes prevention or management. While research in this area continues to evolve, existing studies suggest several mechanisms through which dragon fruit may benefit glucose metabolism.
Animal studies have indicated that compounds in dragon fruit might help lower blood sugar levels by supporting pancreatic health. The pancreas produces insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, and maintaining healthy pancreatic function is crucial for glucose control. Research suggests that dragon fruit may help regenerate damaged cells in the pancreas, potentially improving insulin production and secretion.
The high fiber content in dragon fruit plays a significant role in blood sugar regulation. Dietary fiber slows the absorption of sugars in the digestive tract, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels after meals. This gradual, steady release of glucose helps maintain more stable blood sugar levels throughout the day and reduces the burden on the pancreas to produce large amounts of insulin quickly.
Dragon fruit’s ability to improve insulin sensitivity represents another important mechanism for blood sugar control. Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively cells respond to insulin signals, and improved sensitivity means cells can take up glucose from the bloodstream more efficiently with less insulin required. This reduces the risk of insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
While small studies in people with diabetes have produced inconclusive results, the preliminary evidence remains encouraging. The fruit’s combination of fiber, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds creates a favorable metabolic environment that may support healthy blood sugar levels when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging Benefits
Dragon fruit offers notable benefits for skin health and may help slow visible signs of aging through its rich antioxidant content and nutrient profile. The connection between diet and skin appearance is well-established, and dragon fruit provides several compounds that support healthy, youthful-looking skin.
The antioxidants in dragon fruit, particularly vitamin C, play crucial roles in maintaining skin health. Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis, the protein that provides structure, firmness, and elasticity to skin. Adequate collagen production helps maintain skin’s youthful appearance and supports wound healing and tissue repair.
Free radical damage is a primary contributor to premature aging, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of skin elasticity. The diverse antioxidants in dragon fruit—including betalains, flavonoids, and polyphenols—neutralize free radicals before they can damage skin cells. This protection helps prevent oxidative stress that accelerates aging and contributes to various skin concerns.
The anti-inflammatory properties of dragon fruit’s bioactive compounds may also benefit skin health by reducing inflammation that can contribute to acne, rosacea, and other inflammatory skin conditions. Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a factor in accelerated aging, making dragon fruit’s anti-inflammatory effects valuable for maintaining healthy skin over time.
Dragon fruit’s hydrating properties, due to its high water content, support skin moisture from within. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining skin’s plumpness, suppleness, and overall healthy appearance. While topical hydration is important, internal hydration through water-rich foods like dragon fruit provides fundamental support for skin health.
Iron Absorption and Anemia Prevention
Dragon fruit offers unique benefits for iron absorption and may help prevent iron deficiency anemia, a common nutritional deficiency worldwide. While the fruit itself contains modest amounts of iron, its real value lies in its ability to enhance iron absorption from other dietary sources.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce adequate hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and difficulty concentrating. Dragon fruit addresses this concern through multiple mechanisms.
The vitamin C content in dragon fruit significantly enhances iron absorption, particularly non-heme iron found in plant-based foods. Vitamin C converts iron into a form that is more easily absorbed by the intestines, making it especially valuable for vegetarians and vegans who rely on plant sources for iron. Consuming dragon fruit alongside iron-rich foods can substantially improve iron uptake.
Dragon fruit also contains iron itself, though in relatively small amounts. While one serving may not provide a large percentage of daily iron needs, every contribution matters, particularly when combined with the fruit’s ability to enhance iron absorption from other foods consumed in the same meal.
For individuals at risk of iron deficiency—including women of childbearing age, pregnant women, and those following plant-based diets—incorporating dragon fruit into meals can be a strategic dietary choice. The combination of providing some iron while enhancing absorption of dietary iron makes dragon fruit a valuable component of an iron-optimization strategy.
Bone Health Support
Dragon fruit contributes to bone health through its magnesium content and other bone-supporting nutrients. While often overlooked compared to calcium, magnesium plays crucial roles in bone formation and maintaining bone density throughout life.
Magnesium is involved in converting vitamin D into its active form, which is necessary for calcium absorption. Without adequate magnesium, the body cannot effectively utilize calcium for bone building and maintenance, regardless of calcium intake. Dragon fruit provides approximately 2% of the daily value for magnesium per 100-gram serving, contributing to overall magnesium intake when consumed regularly.
The fruit also contains other minerals that support bone health, including small amounts of phosphorus and potassium. While these amounts are modest, they contribute to the overall nutrient profile that supports skeletal health. Bone health depends on a complex interplay of numerous nutrients working together, and dragon fruit provides several of these essential components.
The antioxidants in dragon fruit may also benefit bone health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can contribute to bone loss over time. Chronic inflammation has been linked to decreased bone density and increased fracture risk, making dragon fruit’s anti-inflammatory properties relevant for long-term bone health.
For optimal bone health, dragon fruit should be consumed as part of a comprehensive dietary approach that includes adequate calcium, vitamin D, protein, and other bone-supporting nutrients. However, its magnesium content and overall nutrient density make it a valuable addition to a bone-healthy eating pattern.
How to Select and Store Dragon Fruit
Choosing and storing dragon fruit properly ensures you enjoy optimal flavor, texture, and nutritional benefits. Understanding how to identify ripe fruit and maintain its quality helps you get the most value from this exotic produce.
When selecting dragon fruit, look for fruit with bright, evenly colored skin without excessive dark spots or bruising. The skin should yield slightly to gentle pressure, similar to a ripe avocado or kiwi. Overly firm fruit is underripe, while fruit that feels mushy is overripe. The scales on the skin should be vibrant and fresh-looking rather than dried or browned.
Ripe dragon fruit should feel relatively heavy for its size, indicating good moisture content and fresh flesh. Light fruit may be dried out or hollow. If purchasing underripe fruit, allow it to ripen at room temperature for several days until it yields to gentle pressure.
Once ripe, dragon fruit can be stored in the refrigerator for up to five days. Place it in a plastic bag or sealed container to prevent it from absorbing odors from other foods. For best flavor and texture, consume refrigerated dragon fruit within this timeframe, as quality deteriorates with extended storage.
Dragon fruit can also be frozen for longer-term storage. Cut the fruit into cubes or slices, place them on a baking sheet to freeze individually, then transfer to freezer bags. Frozen dragon fruit works wonderfully in smoothies, though the texture becomes softer upon thawing, making it less suitable for eating fresh.
Delicious Ways to Enjoy Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit’s mild, refreshing flavor and striking appearance make it incredibly versatile in the kitchen. Whether you prefer simple preparations or creative culinary adventures, there are numerous delicious ways to incorporate this nutritious fruit into your diet.
The simplest method is eating dragon fruit fresh. Cut the fruit in half lengthwise and scoop out the flesh with a spoon, or peel away the skin and slice the flesh into cubes. The seeds are edible and provide a pleasant crunch, similar to kiwi. Fresh dragon fruit makes an excellent snack, breakfast addition, or light dessert.
Dragon fruit smoothies have become increasingly popular, and for good reason. The fruit’s mild flavor blends beautifully with other fruits like mango, pineapple, berries, and banana. Combine dragon fruit with your choice of liquid (coconut water, almond milk, or juice), add other fruits, and blend until smooth for a nutrient-packed smoothie. The red variety creates stunning pink smoothies that are as beautiful as they are nutritious.
Dragon fruit bowls offer an Instagram-worthy breakfast option that’s both nutritious and satisfying. Blend frozen dragon fruit with a small amount of liquid to create a thick, sorbet-like consistency, then top with granola, fresh fruits, nuts, seeds, and coconut flakes. The vibrant color makes for an appealing presentation that encourages healthy eating.
In salads, dragon fruit adds visual interest and subtle sweetness. Cube the fruit and toss it with mixed greens, avocado, cucumber, and citrus vinaigrette for a refreshing tropical salad. Dragon fruit also pairs well with seafood, making it an excellent addition to shrimp or fish salads.
For beverages, dragon fruit can be juiced or blended into refreshing drinks. Combine dragon fruit with lime juice and sparkling water for a healthy, naturally flavored soda alternative. The fruit also works well in cocktails and mocktails, adding both flavor and visual appeal.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While dragon fruit is generally safe and well-tolerated by most people, there are a few considerations and potential side effects to be aware of when incorporating this fruit into your diet.
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to dragon fruit, though this is relatively rare. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include itching, swelling of the lips or tongue, hives, or difficulty breathing. If you’re trying dragon fruit for the first time, start with a small amount to ensure you don’t have an adverse reaction.
The red variety of dragon fruit can cause harmless temporary discoloration of urine or stool, turning them pinkish or reddish. This is due to the betalain pigments and is completely normal and harmless, similar to what occurs after eating beets. The discoloration typically resolves within a day or two.
Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar responses when consuming dragon fruit, as with any fruit. While dragon fruit may have beneficial effects on blood sugar regulation, it still contains natural sugars that can affect glucose levels. Consult with a healthcare provider about appropriate portion sizes if you have diabetes or blood sugar concerns.
Due to limited research on dragon fruit consumption during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it’s advisable to consume it in moderate amounts as part of a varied diet. While there’s no evidence suggesting harm, moderation is always prudent when consuming any food during these periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often should I eat dragon fruit to experience health benefits?
A: There’s no specific recommended frequency, but incorporating dragon fruit into your diet several times per week as part of a varied fruit intake can help you experience its health benefits. Aim for 1-2 servings (approximately 100-200 grams) when you consume it, ensuring it’s part of meeting the recommended 1.5-2 cups of daily fruit intake.
Q: Is dragon fruit suitable for people with diabetes?
A: Dragon fruit can be suitable for people with diabetes when consumed in appropriate portions as part of a balanced meal plan. The fruit’s fiber content helps slow sugar absorption, and research suggests it may support healthy blood sugar levels. However, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose responses and consult with healthcare providers about appropriate serving sizes.
Q: Does the color of dragon fruit affect its nutritional value?
A: Yes, there are nutritional differences between varieties. Red-fleshed dragon fruit contains higher levels of betalains, the antioxidant pigments responsible for its deep color, which provide additional health benefits including enhanced cholesterol-lowering effects. However, all varieties offer valuable nutrients and health benefits.
Q: Can I eat dragon fruit skin?
A: The skin of dragon fruit is technically edible but is typically not consumed due to its tough, leathery texture and bitter taste. The flesh and seeds are the parts commonly eaten. Some people do use the skin for composting or creating natural dyes.
Q: Will eating dragon fruit help me lose weight?
A: Dragon fruit can support weight management efforts due to its low calorie content, high fiber, and ability to promote fullness. However, no single food causes weight loss. Dragon fruit is most effective as part of a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Q: How does dragon fruit compare to other superfruits?
A: Dragon fruit offers unique benefits with its specific combination of antioxidants, particularly its ability to protect fatty acids from oxidative damage. While it may not rank highest in every individual nutrient compared to other superfruits, it provides excellent overall nutritional value, prebiotic fiber, and diverse antioxidants that make it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Q: Can children eat dragon fruit?
A: Yes, dragon fruit is generally safe and nutritious for children. Its mild flavor and soft texture make it appealing to many kids. As with introducing any new food, start with small amounts to ensure there are no allergic reactions, and cut it appropriately for young children to prevent choking hazards.
Q: Where can I buy dragon fruit?
A: Dragon fruit is increasingly available in mainstream supermarkets, particularly in the produce section near other tropical fruits. You can also find it at Asian grocery stores, specialty health food stores, and farmers’ markets. Both fresh and frozen dragon fruit are available, with frozen options being more convenient for smoothies.
The Bottom Line
Dragon fruit stands out as an exceptional addition to a health-conscious diet, offering an impressive array of benefits that extend far beyond its striking appearance. From supporting cardiovascular health and strengthening immunity to promoting healthy digestion and potentially aiding in weight management, this tropical fruit delivers comprehensive wellness support through its unique combination of nutrients, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds.
While dragon fruit shouldn’t be viewed as a magic solution for health concerns, its regular consumption as part of a varied, balanced diet can contribute meaningfully to overall wellness. The fruit’s low calorie content, substantial fiber, diverse antioxidants, and prebiotic properties make it particularly valuable in today’s health landscape where processed foods dominate many diets.
Perhaps most importantly, dragon fruit offers an opportunity to add variety, color, and excitement to your fruit intake, making healthy eating more enjoyable and sustainable. Whether you enjoy it fresh, blended into smoothies, or incorporated into creative recipes, dragon fruit provides both nutrition and culinary pleasure. As research continues to explore this fascinating fruit, its potential as a functional food for supporting metabolic health, preventing chronic diseases, and enhancing overall wellness becomes increasingly clear, making it well worth including in your regular dietary rotation.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/dragon-fruit
- https://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/benefits-dragon-fruit
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11643819/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/dragon-fruit-how-to-enjoy-this-antioxidant-rich-fruit
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/dragon-fruit-benefits
- https://www.dole.com/produce/dragon-fruit
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/get-to-know-the-incredible-edible-dragon-fruit
Read full bio of Medha Deb