Discovering Acai Berry: Nutritional Powerhouse & Health Benefits
Explore the impressive health, beauty, and wellness benefits of the acai berry — nature’s antioxidant-rich superfruit.
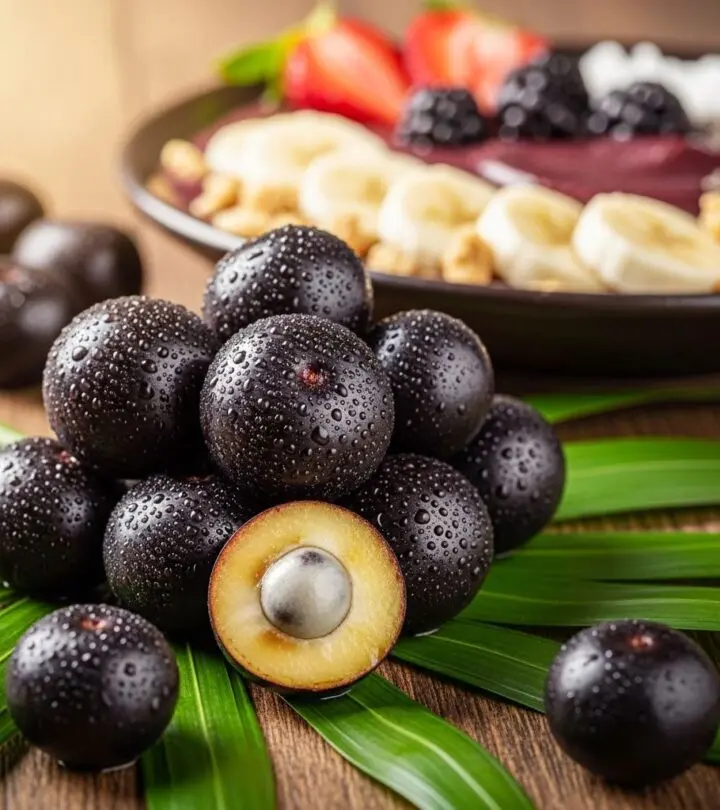

Image: ShutterStock
Introduction to Acai Berry
The acai berry is a small, dark purple fruit that grows on the acai palm (Euterpe oleracea), native to Central and South American rainforests. Celebrated as a superfruit, acai has gained global popularity for its impressive nutritional value and potential health benefits. Pronounced ah-sah-EE, acai berries have been incorporated into both traditional medicine and modern health foods, most notably in the beloved acai bowl.
Acai Berry Nutrition: What Makes It Unique?
Unlike many fruits, acai berries are notable for their high healthy fat content and low sugar levels. They also provide an array of micronutrients and phytochemicals important for overall health.
| Nutrient | Per 100g Frozen Pulp |
|---|---|
| Calories | 70 |
| Total Fat | 5g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g |
| Carbohydrates | 4g |
| Sugar | 2g |
| Fiber | 2g |
| Vitamin A | 15% of RDI |
| Calcium | 2% of RDI |
Acai also contains trace minerals such as chromium, zinc, iron, copper, manganese, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Antioxidant Power: Fighting Free Radicals
Acai berries are among the most antioxidant-rich fruits, surpassing famous contenders like blueberries and cranberries. The deep purple color derives from plant compounds known as anthocyanins, potent antioxidants that neutralize free radicals — molecules implicated in cell damage, aging, and chronic disease.
- ORAC value: Acai’s oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) is 15,405 per 100g, triple that of blueberries.
- Other antioxidant compounds in acai include phenols and flavonoids.
- Regular consumption may help protect cells from stress and reduce chronic disease risk.
Research reveals that acai pulp raises antioxidant levels in the blood, suggesting good absorption of these powerful plant compounds.
Main Health Benefits of Acai Berry
1. Boosts Heart Health
Acai berries are linked to cardiovascular benefits due to their antioxidant and phytosterol content.
- Reduces “bad” LDL cholesterol: Acai may help lower harmful cholesterol that can lead to arterial plaque and heart disease.
- Increases “good” HDL cholesterol: Maintaining healthy HDL cholesterol levels supports cardiovascular health.
- Phytosterols (plant compounds) block cholesterol absorption, further supporting heart health.
2. Supports Brain Function
The antioxidants in acai berries may improve memory and slow age-related mental decline by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation in brain cells. Lab studies have shown acai supplements may slow progression in neurodegenerative conditions by reducing cell death and inflammation, though further human trials are needed.
3. May Aid Digestion
Acai berries contain dietary fiber and bioactive compounds that encourage digestive health.
- Promotes regularity: The fiber content helps maintain bowel movements.
- Supports gut health: Antioxidants and phytochemicals may protect cells lining the digestive tract.
4. Helps Manage Blood Sugar
Some research suggests that acai may help regulate blood sugar in overweight individuals, potentially reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. More studies are needed to clarify optimal intake and efficacy.
5. May Support Weight Loss
Although not a magic bullet, acai berries’ fiber, nutrient density, and potential appetite-regulating properties may support healthy weight management as part of a balanced diet.
- Low in sugar, high in nutrients — ideal for weight-conscious diets
- May curb unhealthy cravings due to nutrient density
Acai for Beauty and Skin Care
Acai oil is increasingly used in cosmetics and beauty products thanks to its antioxidant profile.
- Often found in facial creams, body lotions, anti-aging serums, shampoos, and conditioners
- May protect skin from environmental stress and premature aging
- Acai’s antioxidant levels remain high even after oil extraction and storage
While the evidence is mostly anecdotal, acai oil is considered a safe alternative to many tropical oils used in the cosmetic industry.
Acai Bowls and Foods: Tasty Ways to Enjoy Acai
The most popular way to consume acai outside its native region is the acai bowl — a frozen blend of acai pulp topped with fruits, nuts, seeds, and sometimes granola. The berry is also found in juices, smoothies, dried powders, and supplement form.
- Opt for unsweetened varieties for maximum health benefits.
- Pair acai with vitamin C-rich fruits (like oranges or strawberries) to enhance nutrient absorption.
- Avoid adding excess sugars or calorie-rich toppings if mindful of weight management.
Potential Side Effects & Precautions
Acai berries are generally deemed safe when consumed in food amounts or as supplements. However, excessive intake may cause mild digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
- Allergic reactions are rare.
- Check labels for added sugars or fillers in processed acai products.
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications.
Individuals with chronic kidney disease are advised to consult their doctor before consuming large amounts of acai or acai supplements, as some products may contain minerals not suitable for certain kidney conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is acai berry safe for everyone?
A: Yes, for most people acai is safe in food and supplement forms. However, consult your doctor if you have pre-existing conditions, especially kidney issues.
Q: Can acai berry help with weight loss?
A: Acai is not a fat-burning miracle food but is nutrient-dense and low in sugar; it may support weight loss as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle.
Q: What makes acai different from other berries?
A: Acai berries have more healthy fats, fewer sugars, and significantly higher antioxidant content compared to most other berries.
Q: How do you pronounce acai?
A: The correct pronunciation is ah-sah-EE.
Q: Does acai berry improve skin quality?
A: Acai’s antioxidants may help protect skin and delay signs of aging, though results depend on individual factors and product formulation.
Acai Berry: Uses in Traditional & Modern Medicine
In the Amazon region, acai berries have featured in traditional remedies for centuries to boost energy, fight infection, and improve digestion. Contemporary research continues to examine their effects on metabolic and chronic diseases, although more clinical studies are needed to fully support all claims.
How to Choose High-Quality Acai Products
For the best nutrition and health impact, seek out pure, minimally processed acai foods:
- Frozen acai purée is preferred over acai juice due to higher antioxidant retention.
- Check for products without excess sugar, artificial additives, or preservatives.
- Organic, wild-harvested acai tends to have better nutrient profiles.
Conclusion: Should You Add Acai Berry to Your Diet?
Acai berries are a nutritional powerhouse offering substantial antioxidants, healthy fats, and fiber, plus a wealth of vitamins and minerals. Their potential for supporting heart, brain, digestive, and skin health make them a popular addition to modern diets.
While more human research will help clarify and solidify their unique benefits, acai remains an attractive, tasty, and nutritious fruit that can be a valuable part of a balanced lifestyle.
References
- https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/acai-berries
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/acai-berries-and-acai-berry-juice-what-are-the-health-benefits
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/305576
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/acai-benefits
- https://gatorcare.org/2026/10/14/food-for-thought-are-acai-bowls-healthy/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/benefits-of-acai-berries
- https://nutritionfacts.org/topics/acai-berries/
- https://www.sambazon.com/pages/discover-acai
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9965320/
Read full bio of Medha Deb