Diatomaceous Earth: Uses, Benefits, and Important Safety Tips
Explore the versatile applications, science-backed benefits, and essential precautions of diatomaceous earth for home, health, and garden.
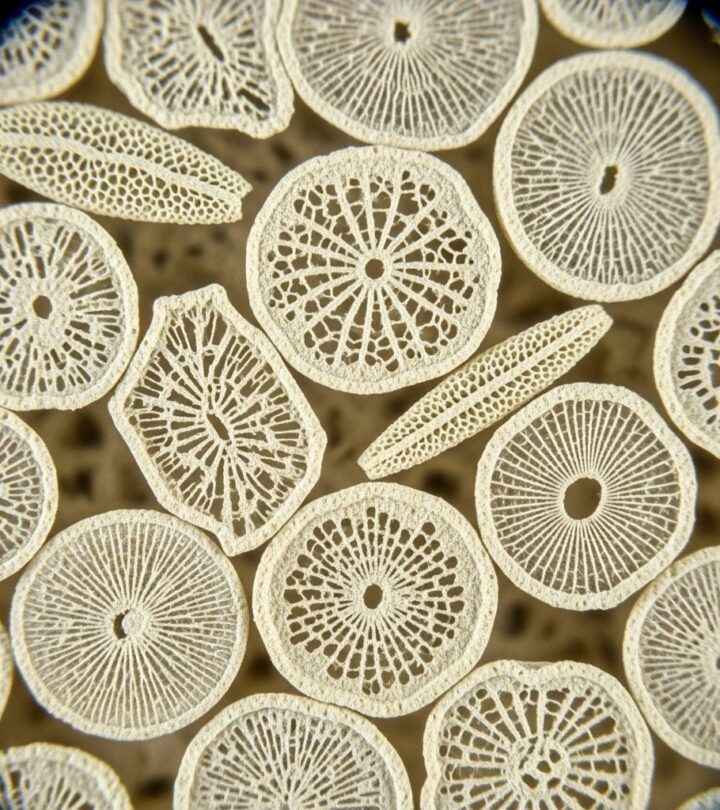
Image: ShutterStock
Diatomaceous earth (DE), a naturally-occurring soft sedimentary rock, is composed of the fossilized remains of microscopic aquatic organisms known as diatoms. With a powdery texture and an impressive range of practical applications, this mineral-rich substance has become increasingly popular in natural health, home, and garden circles. From its unique silica content to its pesticidal properties, DE offers a multitude of benefits—when used with care and understanding. This comprehensive guide explores its composition, health and household benefits, application methods, safety considerations, and more.
What Is Diatomaceous Earth?
Diatomaceous earth is derived from sedimentary deposits of ancient lake and river beds, where the fossilized skeletons of single-celled diatoms accumulate over millennia. Rich in amorphous silica (typically 80–90%), DE also contains minerals such as magnesium, calcium, sodium, iron, and trace elements.
- Appearance: Fine, white or off-white powder.
- Types:
- Food-grade: Suitable for human and animal consumption. Contains low levels of crystalline silica.
- Filter-grade (industrial-grade): Used in filtration, not safe for consumption due to higher crystalline silica content.
Unique Chemical Composition of DE
The two most common types of silica found in DE are:
- Amorphous silica: Non-crystalline and considered safe for humans and pets in food-grade DE.
- Crystalline silica: A harder, sharper form concentrated in industrial-grade DE, which can be hazardous if inhaled in significant quantities.
Health Benefits of Diatomaceous Earth
The following research-backed and anecdotal benefits have made food-grade diatomaceous earth popular in holistic and alternative medicine communities. Always consult a healthcare provider before ingesting DE or starting any new supplement.
1. Natural Detoxification and Digestive Support
DE’s porous structure enables it to bind to toxins, heavy metals, and impurities in the digestive tract, helping with their excretion.
- Cleanses the gastrointestinal tract by trapping and eliminating toxins.
- May help reduce bloating and gas by supporting regular bowel movements and gut health.
- Some proponents report enhanced feelings of energy and well-being due to more efficient toxin clearance.
2. Fights Internal Parasites
Studies suggest that DE can help eliminate internal parasites in livestock and poultry, including intestinal worms.
- A 2011 Oxford Journal of Poultry Science study found improved egg production and lower parasitic infection rates in hens given DE supplements.
- Similar principles are sometimes applied by holistic practitioners recommending DE for pet parasite control.
3. Joint, Bone, and Ligament Health
Silica, the primary component of DE, participates in the formation and maintenance of bones, connective tissue, and cartilage.
- Supports collagen synthesis for flexible, healthy joints.
- May help improve bone mineral density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis (as observed in some clinical studies of dietary silicon).
- Most reports are supportive but more research is needed for conclusive evidence.
4. Supports Hair, Skin, and Nail Health
Food-grade DE is valued for its silica, which is essential for skin elasticity and repair, as well as the growth and resilience of hair and nails.
- Exfoliates skin and removes impurities in topical DE formulations.
- Some oral supplements claim benefits for hair thickness and shinier nails, though such effects are largely anecdotal.
- Used in many natural toothpastes due to its gentle abrasiveness and cleansing properties.
5. May Support Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Limited studies have explored the influence of DE on cholesterol management:
- A small 8-week study in the European Journal of Medical Research observed a significant reduction in total cholesterol, triglycerides, and an increase in HDL cholesterol in adults supplementing with DE.
- Further research is needed to establish these benefits with certainty—consult your doctor for cholesterol management.
Common Uses of Diatomaceous Earth at Home
DE’s abrasive and absorptive qualities make it useful in many household and cleaning contexts.
- Natural Pest Control: Sprinkling DE in cracks, corners, or garden beds deters insects by dehydrating and damaging their exoskeletons. Safe for humans and pets when applied properly.
- Cleaning Agent: Used as a non-toxic, abrasive powder for scrubbing sinks, tubs, and other surfaces.
- Deodorizer:
- Odor-neutralizing in litter boxes, refrigerators, shoes, and carpets.
- Add to trash cans or compost bins to minimize smells and absorb moisture.
- Furniture Polish and Carpet Cleaner: Gently abrasive, making it useful for stain removal and surface buffing.
- Absorbs Oil and Grease: Sprinkle on spills to soak up excess liquid for safer, easier cleaning.
Gardening and Agricultural Applications
- Soil Conditioner: Helps aerate and improve the structure of soil due to its porosity.
- Pest Deterrent: Minimizes insect damage without introducing harmful chemicals.
- Animal Feed Additive: Sometimes added to livestock and poultry feed to reduce parasites and improve eggshell quality. Only food-grade DE should be used.
Innovative and Industrial Uses
Diatomaceous earth also plays a role in various commercial and industrial applications:
- Filtration: Used in water filters and swimming pool filter systems for its remarkable particle-trapping ability.
- Anti-caking Agent: Added to grains and powders to prevent clumping.
- Insulation: Low-density, heat-insulating DE is used in refractory bricks and fireproof safes.
- Cosmetics and Polishes: Added to facial scrubs, toothpastes, and polishes for mild exfoliation and cleaning.
How to Use Diatomaceous Earth Safely at Home
For most uses around the home or garden, food-grade diatomaceous earth is the safest choice. Always read and follow the application instructions, and take precautions to avoid inhalation of fine particulate matter.
General Guidelines for Use
- Pest Control: Lightly dust entry points, garden beds, or pet sleeping areas. Reapply after rain or cleaning.
- Deodorizing: Sprinkle on carpets or in shoes, let sit, and then vacuum or shake out.
- Skin Exfoliation: Mix small amounts with water or a mild cleanser, gently massage onto damp skin, then rinse thoroughly. Avoid eye contact.
- Oral Ingestion: Only consume food-grade DE. Start with small amounts (typically 1 teaspoon mixed with water or juice), gradually increasing to no more than 1 tablespoon daily. Drink plenty of water. Consult your doctor before use, especially if on medication or with chronic conditions.
Possible Side Effects and Important Safety Precautions
While food-grade diatomaceous earth is generally considered safe when used appropriately, certain risks exist, especially when inhaled or consumed in excess.
- Inhalation Hazard: The fine dust can irritate the lungs, especially for those with asthma or other respiratory problems. Wear a dust mask when handling large quantities.
- Eye Irritation: Avoid contact with eyes. Rinse immediately if contact occurs.
- Digestive Discomfort: Consuming excessive amounts may cause bloating, constipation, or other GI discomfort. Start with small quantities.
- Not All Grades Are Safe: Only food-grade DE is safe for human or animal consumption—not industrial or pool-grade DE, which contains hazardous levels of crystalline silica.
Choosing the Right Diatomaceous Earth
| Type | Main Use | Safety for Humans |
|---|---|---|
| Food-grade | Health, household, pets, gardens | Generally recognized as safe |
| Filter-grade (Industrial) | Pools, industrial, filtration | NOT safe for ingestion or breathing |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is it safe to ingest diatomaceous earth?
A: Only food-grade diatomaceous earth is considered safe for limited internal use, provided it is consumed in proper amounts and with plenty of water. Always consult a healthcare professional prior to use.
Q: What pests can DE help control?
A: DE is effective against crawling insects such as ants, cockroaches, bedbugs, fleas, ticks, and some beetles by damaging their exoskeletons and dehydrating them.
Q: Can diatomaceous earth be used on pets?
A: Food-grade DE can be used externally to control fleas and other skin pests on dogs and cats. Avoid the animal’s nose, eyes, and mouth, and consult your veterinarian before internal use.
Q: Does DE interact with medications?
A: DE has the potential to interfere with absorption of some drugs or supplements. Consult your doctor before use, especially if you take regular medications.
Q: Are there any environmental concerns?
A: DE is not toxic to the environment or wildlife when used correctly. Avoid applying near water sources to protect aquatic organisms from excess sediment.
Conclusion: Should You Try Diatomaceous Earth?
Diatomaceous earth is a unique, versatile substance that offers several proven and potential benefits, from non-toxic pest control to digestive health support. However, appropriate selection, safe handling, and realistic expectations are paramount for maximizing its advantages. Always opt for food-grade DE for personal or pet use, follow dosing instructions closely, and observe recommended safety measures. When in doubt, speak with a healthcare or environmental health professional before starting new applications of this fascinating, natural mineral powder.
References
- https://www.amolminechem.com/blog/benefits-of-diatomaceous-earth/
- https://draxe.com/nutrition/diatomaceous-earth/
- https://www.dicalite.com/2025/05/innovative-uses-diatomaceous-earth/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/what-is-diatomaceous-earth
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-diatomaceous-earth
- https://www.agriscigroup.us/articles/ALO-8-114.php
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hoUzQyp_LtA
- https://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/degen.html
- https://lamclinic.com/blog/diatomaceous-earth-potential-uses-cautions/
Read full bio of Sneha Tete














