10 Asparagus Side Effects You Should Know Before Eating Regularly
Understanding the potential risks and drawbacks of regular asparagus intake for optimal dietary health.
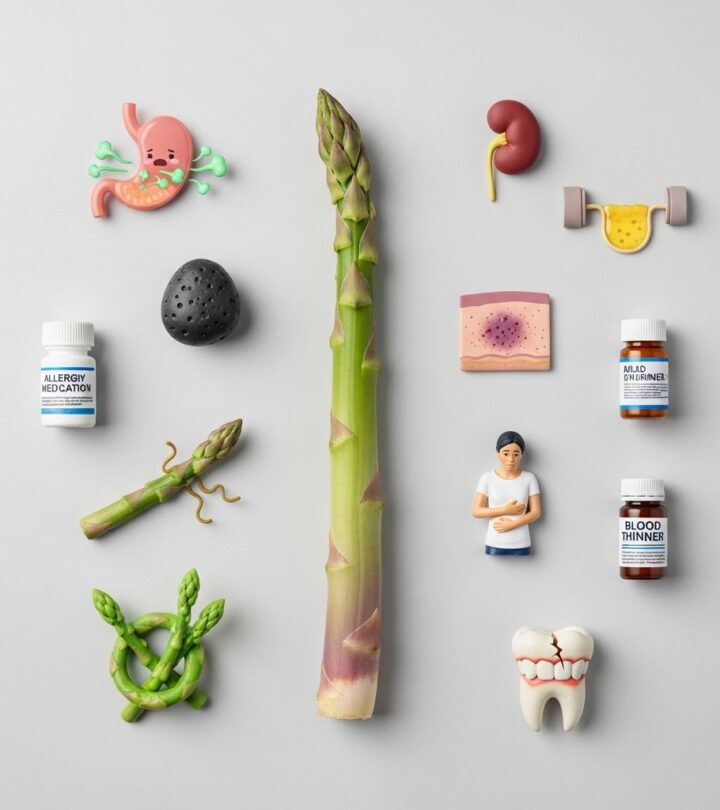
Image: ShutterStock
10 Side Effects of Asparagus You Should Be Aware Of
Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) is a nutritious vegetable beloved for its health benefits and fresh flavor. It supplies vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants making it an excellent choice for balanced diets. However, consuming asparagus can also pose certain risks, particularly for sensitive individuals or those with existing health conditions. Understanding the side effects of asparagus helps you make safe dietary choices and avoid unwanted health problems.
Nutritional Overview of Asparagus
Before delving into side effects, it’s important to consider asparagus’s rich nutritional profile:
- High in fiber, promoting digestive health.
- Excellent source of vitamin B6, vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate.
- Contains beta-carotene, magnesium, calcium, potassium, and chromium (helps regulate blood sugar).
- Low in calories, sodium, and fat.
Despite these nutritional benefits, asparagus may also cause adverse effects for some people. Below are the main side effects you should be aware of.
1. Allergic Reactions
An asparagus allergy may manifest as:
- Skin rash (contact dermatitis)
- Respiratory symptoms (such as wheezing, nasal congestion, sneezing)
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Anaphylaxis—a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction (rare)
People allergic to plants in the Liliaceae family (e.g. onions, garlic, chives, leeks) are at higher risk for asparagus allergy. Symptoms can include swelling around the mouth, lips, and eyes, or even difficulty breathing. Immediate medical attention is required for any severe reaction.
2. Digestive Issues
Asparagus packs substantial fiber, which while beneficial for health, can lead to:
- Bloating
- Flatulence (gas production)
- Stomach cramps
These symptoms are especially noticeable in individuals unaccustomed to high-fiber diets, those with underlying digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or when consuming large quantities of asparagus.
3. Foul-Smelling Urine
Eating asparagus triggers a distinctive, sometimes unpleasant odor in urine. This is due to the metabolic breakdown of asparagusic acid into sulfur-containing compounds. The perception of odor is variable; only some people can smell it due to genetic differences in odorant receptors.
| Cause | Odor Detection | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Asparagusic acid breakdown | Genetically determined | Harmless, but notable |
This effect is benign, but may be alarming for those not expecting it.
4. Medication Interactions
Asparagus may interact with certain drugs, especially those affecting fluid balance and lithium levels:
- Lithium: Asparagus’s diuretic effect may reduce the kidney’s ability to remove lithium, raising blood lithium to toxic levels. If you take lithium, consult your healthcare professional before eating asparagus regularly.
- Diuretic drugs (“water pills”): Combined use can lower potassium dangerously, causing weakness or heart complications.
Caution is warranted if you’re on medication affecting fluid or electrolyte balance.
5. Hormonal Effects and Pregnancy Concerns
While eating asparagus as food during pregnancy is considered safe, asparagus extracts may influence hormonal functions. Historically, some traditional medicines used asparagus extracts as a form of birth control, which could disrupt hormone balance and negatively affect pregnancy outcomes.
- Avoid asparagus extracts during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Stick strictly to food amounts if you’re pregnant.
6. Risk for Those with Allergies to Liliaceae Family Plants
If you’re allergic to onions, leeks, garlic, or chives (also in the Liliaceae family), you may be at increased risk for an allergic reaction to asparagus.
- Symptoms: Skin rash, swelling, respiratory distress
- In rare cases: Oral allergy syndrome (itching or burning of mouth/throat after consuming asparagus)
Consult an allergist if you suspect cross-reactivity.
7. Kidney Stone Risk Due to Purine Content
Asparagus contains purines, which break down into uric acid. Excess intake can increase the possibility of developing uric acid kidney stones in those predisposed to this condition. If you’ve had gout or uric acid kidney stones, eat asparagus in moderation.
| Condition | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| Gout/history of kidney stones | Elevated; moderation needed |
| Average healthy individual | Very low |
8. Estrogenic Effect and Female Hormonal Imbalance
Some compounds in asparagus extracts (especially Ayurvedic Shatavari preparations) are believed to have estrogenic effects. Overconsumption or use of concentrated supplements may potentially disrupt hormone levels in women, particularly those with hormone-sensitive conditions like breast cancer, endometriosis, or ovarian cysts.
- If you have a hormone-sensitive condition, discuss asparagus supplements with a healthcare provider.
9. Incomplete Safety Data on Excess Consumption
Studies evaluating the safety of asparagus at high doses (as food or supplements) are limited. While moderate food intake is recognized as safe, excessive use in therapeutic doses may pose unknown risks—including possible digestive disturbance, electrolyte imbalance, and allergic reaction.
- Stay within normal dietary amounts.
- Be cautious with asparagus supplements or extracts; insufficient data supports their extensive use.
10. Skin Sensitivity and Contact Dermatitis
Occupational exposure to fresh asparagus (farmers, cooks, kitchen workers) occasionally causes contact dermatitis—itching, redness, blisters on skin. This is typically seen in people with existing plant allergies.
- Wear gloves while handling raw asparagus if you notice skin irritation.
- Seek medical advice if dermatitis develops.
FAQs About Asparagus Side Effects
Q: Is asparagus safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
A: Asparagus as food is considered safe, but avoid asparagus extracts or medicinal amounts during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to possible hormone disruption.
Q: Why does asparagus make my urine smell?
A: Asparagusic acid in asparagus is metabolized into sulfurous compounds, producing a distinct odor in urine. Only people with certain odor receptor genes are able to detect this smell.
Q: Can I eat asparagus if I have a history of kidney stones?
A: Asparagus contains purines, which can raise uric acid levels. If you have gout or a history of uric acid kidney stones, moderate your intake and consult a nephrologist.
Q: Are asparagus supplements safe?
A: There is insufficient scientific evidence to support the broad use of asparagus supplements or extracts. Use only under advice from a healthcare professional.
Q: Can asparagus interact with prescription medications?
A: Yes. It can interfere with lithium and certain diuretics, potentially causing drug toxicity or electrolyte imbalance. Always inform your doctor if you eat asparagus regularly and take such medications.
Optimizing Safe Asparagus Consumption
- Moderate intake is best—enjoy asparagus as part of your diet, but avoid excessive amounts, particularly as extracts or supplements.
- Check for allergies—if you experience itching, rashes, or breathing difficulty after eating asparagus, seek medical attention.
- Stay informed—discuss diet changes with your doctor, especially if you have chronic illness or take prescription medications.
- Be cautious with pregnancy—consult your doctor about asparagus consumption.
Summary Table: Side Effects of Asparagus
| Side Effect | Risk Group | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Allergy | Liliaceae family allergies | Test in small amounts; avoid if allergic |
| Digestive upset | High-fiber sensitive individuals | Start slow; hydrate well |
| Urine odor | Genetically determined | No action required |
| Drug interactions | Lithium, diuretics users | Consult physician |
| Hormonal disturbance | Pregnant, hormone-sensitive women | Avoid extracts; consult physician |
| Kidney stone risk | Gout, stone history | Monitor portion; seek medical advice |
| Contact dermatitis | Occupational exposure | Wear gloves; treat skin promptly |
References
- WebMD: Asparagus – Uses, Side Effects, and More
- MedicineNet: What Happens If You Eat Asparagus Every Day?
- Vinmec: Is it safe to eat raw asparagus?
- ICICI Lombard: Asparagus Side Effects: Potential Health Concerns and Risks
- Medical News Today: Asparagus: Nutrition, benefits, and risks
References
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-286/asparagus
- https://www.medicinenet.com/what_happens_if_you_eat_asparagus_every_day/article.htm
- https://www.livescience.com/45295-asparagus-health.html
- https://www.icicilombard.com/blogs/health-insurance/mb/what-are-the-side-effects-of-asparagus
- https://www.vinmec.com/eng/blog/is-it-safe-to-eat-raw-asparagus-en
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/270805
- https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/side-effects-of-asparagus-you-should-be-aware-of/
Read full bio of Sneha Tete














