Aronia Berry Benefits: Nutrition, Uses, and Health Impact
Explore the scientifically backed benefits of aronia berries, their nutrients, uses, side effects, and FAQs.
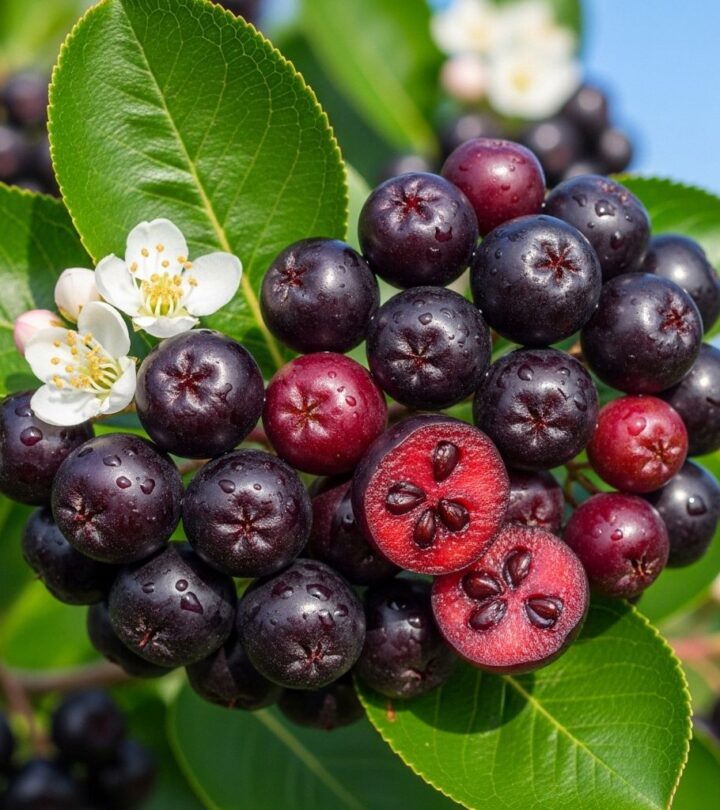

Image: ShutterStock
Aronia berries, also known as chokeberries, have attracted attention as a nutrient-dense superfood, prized for their distinctive flavor and exceptionally high antioxidant content. This article examines the nutrition profile of aronia, outlines the research-backed health benefits, discusses traditional and modern uses, and warns of potential side effects.
What Are Aronia Berries?
Aronia berries are small, dark berries native to North America and now grown in many parts of the world. Belonging to the Rosaceae family, they grow on deciduous shrubs. The fruits have a tart, astringent flavor, explaining the nickname “chokeberry.” Despite their sharp taste, aronia berries are safe to eat and have been valued both for culinary and medicinal purposes since indigenous times.
Nutritional Value of Aronia Berries
Aronia berries are recognized for their high concentration of nutrients and bioactive compounds. Here’s a snapshot of their key nutritional components:
- Antioxidants: Extremely high levels, especially anthocyanins and procyanidins
- Vitamin C: Supports immune function
- Vitamin A, E: Essential vitamins for vision, immunity, and skin health
- Fiber: Promotes digestive health
- Manganese: Mineral important for enzyme function and metabolism
- Potassium and Zinc: Electrolyte and immune-supportive minerals
- Low in sugar (especially compared to other berries)
This unique nutrient profile makes aronia berries an excellent addition to a balanced, antioxidant-rich diet.
Top 10 Science-Backed Health Benefits of Aronia Berries
Extremely High Antioxidant Capacity
Aronia berries contain some of the highest concentrations of polyphenols and anthocyanins found in fruit. Their ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) score is more than three times that of blueberries, making them exceptional for combating oxidative stress and preventing cell damage.
Promote Heart Health
Several studies have demonstrated the cardioprotective potential of aronia berries:
- Aronia extract can help lower blood pressure, reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, and decrease triglyceride levels.
- Polyphenols in aronia may reduce arterial inflammation and decrease blood clot formation.
- Habitual consumption has been linked to improved lipid profiles and favorable changes in DNA methylation associated with a reduced cardiovascular risk.
Support Immune Function
Thanks to their extremely high polyphenol content – especially oligomeric procyanidins (OPCs) – aronia berries help strengthen the immune system. Polyphenol extracts from aronia have shown immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially helping the body fight off infections, including influenza viruses.
Have Anticancer Potential
Laboratory studies suggest that aronia berries may slow the growth of certain cancer cells and reduce cell damage. Extracts have shown promising effects against colon and breast cancer cells in experimental models, though conclusive evidence in humans is still needed.
Promote Healthy Blood Sugar and Improve Insulin Sensitivity
Early animal studies indicate that aronia berries may help fight insulin resistance and improve glucose metabolism, suggesting a role in diabetes management. Further research in humans is needed.
Help Prevent and Manage Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
With five to ten times more quinic acid than cranberries, aronia berries are highly effective in reducing UTI-causing bacteria. A long-term pilot study in older adults showed a 55% reduction in incidence of UTIs, along with decreased antibiotic usage.
May Support Organ Health
Preliminary animal studies indicate that regular intake of aronia juice may help support healthy liver function after damage and protect against the harmful effects of certain chemicals. Aronia’s antioxidants also may provide broad cellular defense, supporting organs such as the stomach, liver, and cardiovascular system.
Reduce Inflammation
Aronia berries’ dense concentration of polyphenols and flavonoids help reduce inflammation throughout the body, potentially offering relief for chronic inflammatory diseases and slowing age-related tissue damage.
Promote Digestive Health
Due to their high fiber content, aronia berries support regular bowel movements and help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, improving overall digestive health.
Natural Source of Vitamins and Minerals for General Wellness
With vitamins C, A, E, and minerals such as potassium and zinc, aronia berries provide essential nutrients that support immunity, energy production, and healthy skin.
Aronia Berry in Traditional and Modern Medicine
Native American tribes have long used aronia berries to make medicinal teas, relieve colds, and as a vitamin-rich food source. Today, scientific research supports many of these traditional uses, and modern supplements and extracts are available for targeted health effects.
Key Bioactive Compounds in Aronia
- Anthocyanins: Potent antioxidants responsible for deep purple coloring
- Procyanidins and Flavonoids: Provide anti-inflammatory and immune benefits
- Ursolic Acid and Quercetin: Studied for antiviral and anti-inflammatory actions
- Quinic Acid: Backed for UTI prevention
These compounds may work synergistically to boost immunity, fight oxidative stress, and protect cardiovascular health.
How to Use Aronia Berries
Aronia berries are versatile and can be enjoyed in several ways:
- Fresh: Enjoy raw, though the astringency is strong.
- Juice: Commercial aronia juice is popular; dilute for milder flavor.
- Dried: Mixed into granola, yogurt, oatmeal, or trail mixes.
- Jams/Sauces: Their tartness pairs well with sweeteners.
- Baked Goods: Use in muffins, breads, and pies for a nutrition boost.
- Powder: Add to smoothies, shakes, or energy bars.
- Supplement Form: Capsules and extracts are available for targeted health applications.
How to Select and Store Aronia Berries
- Select plump, deep purple or black berries for optimal nutrient density.
- Store fresh berries refrigerated and use within several days.
- Freeze for long-term storage or purchase as dried, powdered, or juiced.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Digestive Discomfort: Consuming large amounts may cause mild gastrointestinal issues (bloating, flatulence).
- Allergic Reaction: Rare, but possible in susceptible individuals.
- Blood Thinning: The high vitamin K and antioxidant content could potentially interact with blood-thinning medications—consult a healthcare provider if taking anticoagulants.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While generally safe in food amounts, always check with a healthcare provider before consuming supplements.
Comparison Table: Aronia vs. Blueberry vs. Cranberry
| Berry | Key Antioxidants | ORAC Value | Main Health Benefit | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aronia | Anthocyanins, Procyanidins, Flavonoids | Very High (3x blueberry) | Cardiovascular & Immune Support | Tart, Astringent |
| Blueberry | Anthocyanins, Vitamin C, Polyphenols | High | Brain & Heart Health | Sweet, Mildly Tart |
| Cranberry | Proanthocyanidins, Quinic Acid | Moderate | UTI Prevention | Very Tart, Slightly Bitter |
Simple Ways to Add Aronia Berries to Your Diet
- Blend aronia powder into smoothies with banana, apple, and spinach.
- Add dried aronia to trail mixes for a tart flavor boost.
- Mix aronia juice with sparkling water and lemon for a refreshing drink.
- Bake aronia berries into muffins or oat bars for natural color and nutrients.
- Use aronia compote as a topping for yogurt or pancakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What does aronia berry taste like?
A: Aronia berries have a tart, astringent flavor that dries the mouth, hence the nickname “chokeberry.”
Q: Are aronia berries safe to eat raw?
A: Yes, they are safe to eat raw, though their strong flavor leads many to prefer them cooked or blended with other foods.
Q: Can aronia berries help prevent disease?
A: Many studies suggest that aronia berries’ antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds may help lower disease risk, but further clinical studies in humans are needed for definitive conclusions.
Q: How much aronia berry should I consume for health benefits?
A: There is no official guideline, but incorporating a handful daily as fresh fruit, juice, or in recipes is generally suggested as a safe, healthful amount for most adults.
Q: Who should avoid aronia berries?
A: Individuals with known berry allergies or those taking blood-thinning medication should consult a healthcare provider before regular use.
Takeaway
Aronia berries stand out among superfruits for their extraordinary antioxidant density, versatile health benefits, and traditional roots in both native healing and modern diets. Add them to your meals or enjoy as a supplement—but, as with any food, moderation and variety are key to reaping their full potential.
References
- https://www.indigo-herbs.co.uk/natural-health-guide/benefits/aronia-berries
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-aronia-berries
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9696386/
- https://extension.sdstate.edu/make-aronia-berries-part-your-healthy-diet
- https://www.mckaynursery.com/mckay-green-tips/learn-about-the-health-benefits-of-aronia-berries
- https://naturehills.com/blogs/garden-blog/health-benefits-of-aronia-berries
- https://www.montanaberries.org/aronia-berries
Read full bio of Sneha Tete