Acerola (Barbados Cherry): Nutrition, Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
Unlock the powerful health benefits, nutritional profile, and best uses of acerola, the vitamin C superfruit from the tropics.
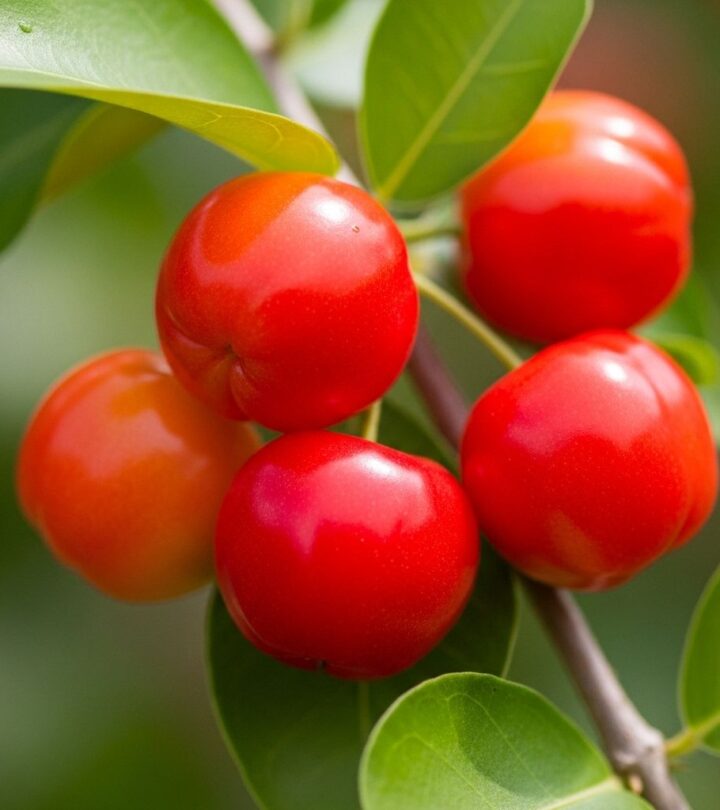

Image: ShutterStock
Acerola (Malpighia emarginata), commonly known as Barbados cherry or West Indian cherry, is a tropical and subtropical fruit celebrated for its exceptional vitamin C content and a wide array of health-enhancing phytonutrients. Native to the Caribbean, Central, and South America, acerola is steadily gaining global recognition as a functional superfruit with remarkable nutritional and therapeutic potential.
What Is Acerola?
Acerola is a small, cherry-like fruit native to tropical regions of the Americas. Also known as Barbados cherry, West Indian cherry, or simply acerola cherry, it thrives in warm climates and matures into a bright red fruit with tart, juicy flesh. Despite its resemblance to regular cherries, acerola has a distinct tartness and is famous for its abundance of vitamin C and plant-based antioxidants.
- Botanical Name: Malpighia emarginata
- Common Names: Barbados cherry, West Indian cherry
- Family: Malpighiaceae
- Native Regions: Caribbean, Central and South America
Nutrition Profile of Acerola
Acerola is lauded as one of the world’s richest natural sources of vitamin C, outpacing oranges and lemons by 50–100 times. Its nutritional spectrum includes a wealth of complementary nutrients and phytochemicals, further amplifying its functional food status.
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100g) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 1500-4500 mg | Immune strength, antioxidant |
| Vitamin A | ~767 IU | Vision, skin, immune health |
| Carotenoids | 9.4–40.6 μg β-carotene equivalents | Antioxidant, eye health |
| Phenolics | Up to 90 mg | Cell protection, aging reversal |
| Anthocyanins | – | Free radical scavenging |
| Minerals (Potassium, Iron, etc.) | Moderate | Cellular function |
| Fiber | ~1.1 g | Digestive support |
Key Phytochemicals in Acerola
- Flavonoids: Quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin
- Carotenoids: Beta-carotene, lutein, beta-cryptoxanthin, alpha-carotene
- Phenolic acids: Ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, hydroxycinnamic acids
- Anthocyanins: Natural pigment antioxidants
- Pectin: Soluble fiber with cholesterol-lowering effects
Health Benefits of Acerola
The potent nutritional profile of acerola translates into a broad range of health-promoting effects, particularly due to its rich vitamin C, phytonutrient, and antioxidant content.
1. Extreme Vitamin C Potency and Immune Support
Acerola is globally recognized as one of the richest natural vitamin C sources. Vitamin C is necessary for collagen synthesis, wound healing, iron absorption, and robust immune defense against pathogens.
- Just 1–2 acerola cherries can fulfill the daily vitamin C requirement for adults.
- Comparable or superior to camu camu, far exceeding citrus fruits in ascorbic acid content.
2. Powerful Antioxidant Action
The fruit’s blend of ascorbic acid, flavonoids, carotenoids, and anthocyanins delivers antioxidant protection against free radical damage. This contributes to reduced cellular aging, healthier skin, and lowered risk of chronic diseases.
3. Skin Health and Anti-Aging Benefits
- Supports collagen production for skin elasticity and firmness.
- Helps reduce visible signs of aging like wrinkles and fine lines.
- May promote skin whitening and lighten dark spots via antioxidant mechanisms.
4. Enhances Wound Healing
- Vitamin C is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration.
- Regular acerola intake can accelerate recovery from injuries and wounds.
5. Supports Eye Health
- Carotenoids (beta-carotene, lutein) help protect eye tissues from oxidative stress.
- May lower the risk of age-related macular degeneration and night blindness.
6. Heart Health and Cholesterol Regulation
- Rich antioxidants help decrease inflammation and protect blood vessels.
- Soluble fiber (pectin) in acerola may help lower bad cholesterol (LDL).
7. Boosts Brain and Cognitive Function
- Chronic oxidative stress in the brain is implicated in cognitive decline.
- Antioxidant-rich foods like acerola can help maintain mental sharpness.
8. Natural Energy and Metabolism Support
- B vitamins and vitamin C play essential roles in energy production and metabolic efficiency.
- Can help combat fatigue and support active lifestyles.
9. Immune Strength and Disease Prevention
- Regular consumption is linked to improved resistance against colds and infections.
- May contribute to reduced severity and duration of illnesses like the common cold.
Traditional and Modern Uses of Acerola
Acerola has been valued for generations in folk medicine for treating a variety of conditions, while its modern uses extend into nutritional, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical products.
Traditional Uses
- Remedy for coughs, colds, and fever
- Topical treatment for wounds and ulcers
- Support for digestive health
Modern Applications
- Vitamin C supplements (powders, capsules, gummies)
- Infused in juices, smoothies, and functional beverages
- Ingredient in jams, jellies, sauces, and desserts
- Used in cosmetics for skin-lightening and anti-aging formulations
- Natural food coloring due to red pigments (anthocyanins)
How to Include Acerola in Your Diet
Acerola can be consumed in various forms. Since the fresh fruit is highly perishable, it is often available as frozen puree, juice, powder, or extract.
- Fresh fruit: Eat raw (if available locally).
- Powder: Add to smoothies, juices, water, or yogurt.
- Frozen pulp: Blend into drinks or desserts.
- Juice: Drink as-is or mix with other fruit juices.
- Supplements: Available as chewable tablets, capsules, and gummies.
Serving Tips
- Acerola pairs well with sweet fruits to balance its tartness (e.g., banana, mango).
- Use powder form for a concentrated vitamin C boost.
- Start with small amounts if new to the fruit—its vitamin C content is very high.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
For most people, acerola is safe when consumed in food amounts. However, excessive intake (especially in supplement form) can lead to some side effects due to its very high vitamin C concentration.
- Digestive upset: Large doses may cause stomach cramps, diarrhea, or nausea.
- Kidney stones: High vitamin C intake can potentially increase oxalate and uric acid, raising the risk of kidney stones in susceptible individuals.
- Interactions: May interact with medications or conditions sensitive to high vitamin C—consult a doctor if you are on medication or have chronic illnesses.
Who Should Avoid Acerola?
- Individuals with kidney disorders: Consult a healthcare professional before use.
- People prone to kidney stones: Excess vitamin C may aggravate risk.
- Those on vitamin C-restricted diets: Should avoid or strictly limit intake.
How to Select and Store Acerola
- Fresh fruit: Look for firm, bright red fruit without blemishes.
- Powder: Choose organic, 100% acerola powder with no fillers.
- Juice/puree: Ensure no added sugars or artificial preservatives.
- Store fresh acerola refrigerated and use within a few days. Powder and supplements should be kept in a cool, dry place.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is acerola the same as cherry?
No. While acerola resembles cherries, it is botanically unrelated and nutritionally far superior in vitamin C and antioxidants.
Q2: How much vitamin C is in acerola?
Fresh acerola contains between 1500–4500 mg of vitamin C per 100 grams—up to 100 times more than oranges or lemons.
Q3: Can acerola supplements replace my multivitamin?
Acerola supplements provide concentrated vitamin C and antioxidants but may lack the balance of other vitamins and minerals found in comprehensive multivitamins.
Q4: What does acerola taste like?
Acerola has a bright, tart, and slightly sweet flavor, often considered more sour than typical cherries.
Q5: Are there risks to eating too much acerola?
Consuming acerola in normal dietary amounts is safe, but excessive vitamin C intake via acerola supplements can cause digestive upset or increase the risk of kidney stones.
Summary Table: Acerola at a Glance
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Malpighia emarginata |
| Common Names | Barbados cherry, West Indian cherry |
| Main Benefit | World’s richest natural source of vitamin C |
| Supporting Nutrients | Carotenoids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, phenolics, fiber |
| Key Uses | Supplements, juices, beauty products, desserts |
| Precautions | Excess intake may cause side effects due to high vitamin C |
Takeaway
Acerola stands as a nutritional powerhouse in the fruit world, with unmatched vitamin C content and a vast arsenal of antioxidants and phytonutrients. It not only fortifies the immune system and supports vitality but also offers potential benefits for skin health, heart function, cognitive support, and more. As interest in natural superfoods grows, acerola is poised to become a staple for those seeking holistic and robust wellbeing.
References
Read full bio of Sneha Tete